THE BIG UGLY
A LOT OF USEFUL INFORMATION
IN A NOT SO GREAT FORMAT
ABOUT THE AMERICAN WORKPLACE
COST OF LVING IN THE NEW YORK AREA
WITH DIFFERENT TERMS AND POSITION DESCRIPTIONS+
The American Worker
Has Very Few Rights


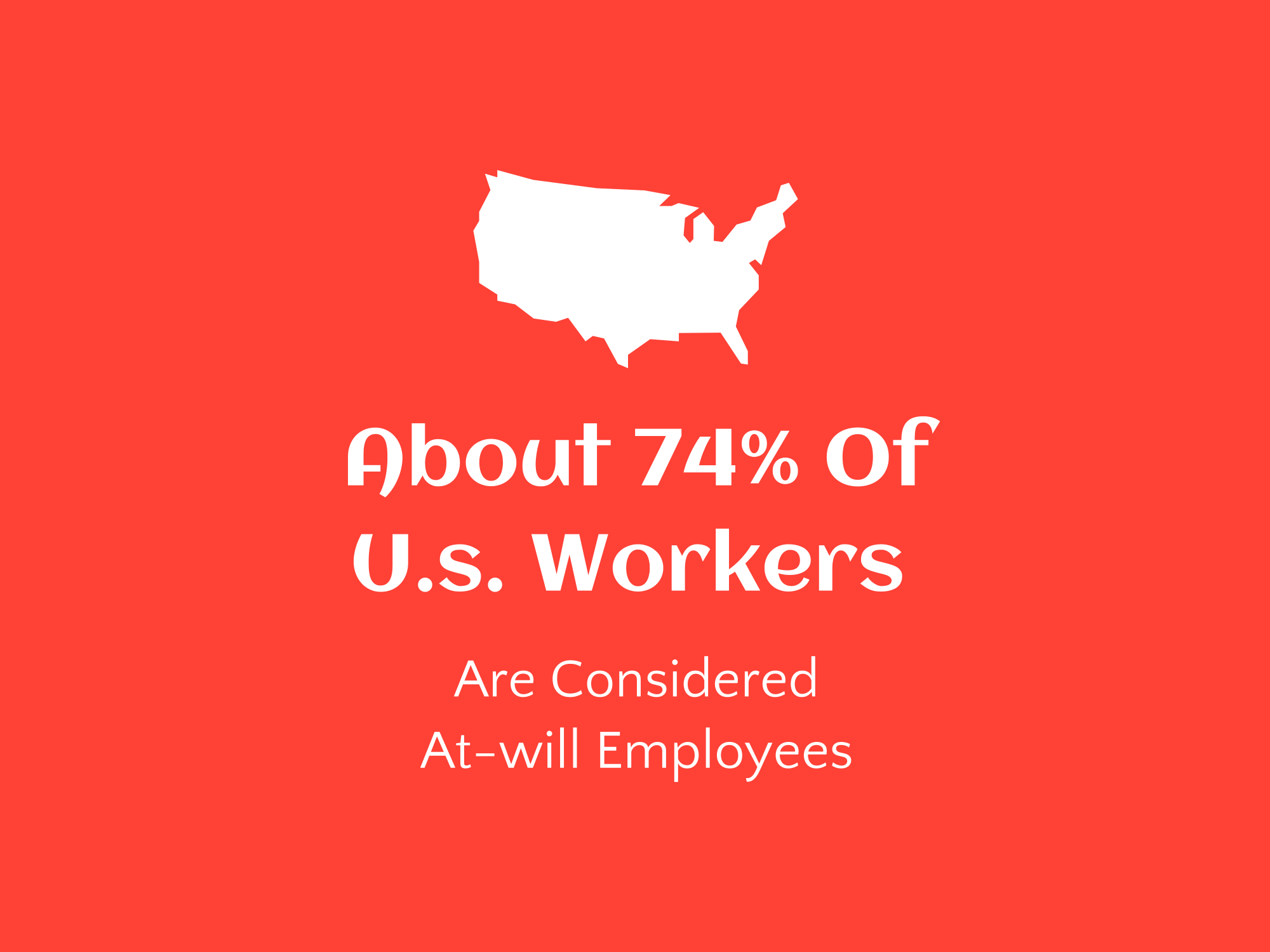
According to a survey by the National Employment Law Project (NELP), around 69% of workers who were fired reported losing their jobs “for no reason or for an unfair reason,” indicating a significant portion of the US workforce experiences job loss without a clear cause; however, the exact number of workers losing jobs without cause is difficult to pinpoint due to the nature of “at-will” employment in most states, allowing employers to terminate without a specific reason

Many employees believe that human resources are there to support them. However, their main role is to protect the employer. HR handles issues like disputes and policy violations, often prioritizing the company’s needs over individual concerns. While they may offer assistance, their loyalty lies with the organization. This balance can lead to misunderstandings about their true function. Employees need to recognize that HR is not just a supportive ally but also a safeguard for the employer’s interests.

The role of an employee is to perform their job duties to the best of their ability in order to contribute to the success of the company they work for. Employees play a crucial part in the everyday operations of a business, whether it be completing tasks, providing excellent customer service, or collaborating with coworkers. It is important for employees to be reliable, responsible, and professional in their work in order to help the company achieve its goals. By fulfilling their role as an employee, individuals can help their company thrive and succeed in the competitive business world.

The role of an employer is to provide jobs and opportunities for people to work and earn money. Employers also have a responsibility to create a safe and fair work environment for their employees, where they can feel respected and supported. Employers are also responsible for setting goals and expectations for their employees, as well as providing feedback and guidance to help them succeed in their roles. Overall, the role of an employer is to help their employees grow and develop, while also ensuring the success and profitability of their business.

Employment at will is a principle of employment law in the United States that allows employers to terminate an employee at any time and for any reason, as long as the reason is not illegal. This means that employees can also resign from their position at any time without reason. While this doctrine provides flexibility for both employers and employees, it has been criticized for potentially leading to unfair treatment and arbitrary dismissals. Despite its limitations, employment at will remains a foundational concept in American labor relations and continues to shape the employer-employee dynamic in the workplace. Graduates of higher education institutions should be aware of the potential implications of this principle as they navigate the job market and negotiate employment contracts in order to protect their rights and interests.
The Frontline For Unions & Thier Members

The role of a union member is to work together with other workers to make sure that everyone is treated fairly and has good working conditions. Union members also help negotiate with employers to make sure that workers are paid a fair wage and have benefits like health insurance and vacation time. Being a union member also means standing up for yourself and your coworkers when there are issues in the workplace, like unsafe working conditions or unfair treatment. By joining a union and being an active member, workers can have a stronger voice in the decisions that affect their work and improve their lives.

Union shop stewards play a vital role in representing and advocating for the rights and interests of union members in the workplace. They act as a liaison between workers and union leadership, ensuring that grievances are heard and addressed in a timely and effective manner. Shop stewards also work to educate members on their rights under the union contract, provide guidance on workplace issues, and promote solidarity among employees. In addition to serving as a voice for workers, stewards may also participate in negotiating collective bargaining agreements, resolving disputes, and serving on union committees. Their role requires strong communication and problem-solving skills, as well as a thorough understanding of labor laws and union policies. Ultimately, shop stewards play a critical role in maintaining a fair and equitable work environment for all union members.

The role of a work supervisor is to oversee and manage employees in a workplace. They are responsible for assigning tasks, coaching and guiding employees, and making sure work is completed efficiently and effectively. Supervisors also play a key role in providing feedback, resolving conflicts, and ensuring that all employees follow company policies and procedures. Overall, work supervisors are essential in maintaining a positive work environment and helping employees thrive in their roles.

Progressive discipline in the workplace is a system where employees are given opportunities to improve their behavior or performance before more serious consequences are imposed. This means that if someone makes a mistake or breaks a rule, they might first receive a verbal warning, then a written warning, and finally suspension or termination if the problem continues. This approach is meant to be fair and give people a chance to learn from their mistakes and make changes. It also helps employers make sure they are following the rules and being consistent in how they deal with problems. Progressive discipline can help create a positive work environment where people feel motivated to do their best and are treated fairly.
The 2nd Line
A union representative is like a superhero for workers. They make sure that everyone in the workplace is treated fairly and that their rights are protected. If there’s a problem at work, like unfair pay or unsafe conditions, the union rep steps in to fight for what’s right. They listen to workers’ concerns, negotiate with the boss, and make sure everyone is treated with respect. Being a union rep is a big responsibility, but it’s also really important because it helps make sure that everyone has a voice at work.

The role of human resources is important in a company because they are the ones who take care of all the people who work there. Human resources helps hire new employees, make sure everyone gets paid, and solve any problems between workers. They also help with training and making sure that all the rules and regulations are followed. Basically, human resources is like the friend at work who looks out for everyone and makes sure things run smoothly.

Unions and employers often hold regular labor management meetings to discuss various issues related to the workplace, such as wages, working conditions, and benefits. These meetings provide a forum for both parties to communicate their concerns, negotiate agreements, and resolve conflicts in a constructive and collaborative manner. By fostering open dialogue and mutual understanding, labor management meetings can help to build trust and improve the overall relationship between unions and employers. This proactive approach to labor relations can lead to more harmonious and productive workplaces, ultimately benefiting both employees and businesses. Overall, regular meetings between unions and employers demonstrate a commitment to effective communication and cooperation in the pursuit of shared goals.
Positions & Their Roles + Responsibilities

The role of a union president is crucial in ensuring the protection of workers’ rights, advocating for fair wages and benefits, and addressing workplace injustices. The president serves as the voice of the union members, negotiating with management on behalf of the workers, and working to improve working conditions and create a safe and equitable environment. The president also plays a key role in strategizing and organizing collective actions, such as strikes or protests, to address labor disputes and push for necessary changes. Overall, the union president holds a position of power and responsibility in championing the interests and well-being of the union members, and is instrumental in promoting solidarity and unity within the organization.

The role of a union executive board is to represent the interests of the union members and make decisions on their behalf. They are responsible for negotiating and enforcing collective bargaining agreements, handling grievances and disputes, and advocating for better working conditions, wages, and benefits for the workers. The executive board also plays a key role in strategic planning, budgeting, and overseeing the overall operation of the union. Essentially, they act as the leaders and decision-makers of the union, working to ensure that members are treated fairly and receive the support they need in the workplace.

As the union operations director, one assumes a crucial role in overseeing and coordinating the day-to-day activities of a labor organization. This position requires a deep understanding of union policies, procedures, and strategic goals. The operations director is responsible for managing staff, developing budgets, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations. Additionally, this role involves working closely with union leadership to drive organizational growth and success. The operations director must possess strong leadership skills, excellent communication abilities, and a knack for problem-solving in order to effectively navigate the complexities of labor relations and advocacy. In essence, the role of a union operations director is essential in ensuring the smooth functioning and success of a labor union.

The role of a union organizing director is super important because they help workers come together to make sure they are treated fairly at work. They talk to employees about problems they might have at work and help them figure out how to fix them. Organizing directors also help plan strikes or protests if workers aren’t being treated right. They work hard to make sure workers have a voice and can stand up for themselves. Overall, union organizing directors play a big role in making sure workers are treated with respect and fairness on the job.

The role of a research and communications director is essential in an organization as they are responsible for gathering and analyzing data, conducting studies, and monitoring trends to provide valuable insights to the decision-makers. They play a crucial role in shaping the communication strategies of the organization by ensuring that the messages are clear, accurate, and tailored to the target audience. Additionally, they are responsible for managing the organization’s public image through effective communication channels such as social media, press releases, and newsletters. Overall, a research and communications director plays a pivotal role in enhancing the organization’s reputation and credibility through strategic planning and communication efforts.

The role of a union political director is super important because they help make sure that workers’ rights are protected and that laws are passed to benefit workers. They work with politicians and government officials to make sure that workers’ voices are heard and that laws are fair. They also help organize campaigns to support candidates who are pro-worker and fight against those who want to take away workers’ rights. Overall, the union political director plays a big role in fighting for workers and making sure their needs are met by the government

The role of a membership strength director is to keep track of the number of members in an organization and come up with ways to attract new members and keep existing ones engaged. They work closely with the leadership team to set goals for increasing membership and create strategies to achieve those goals. Membership strength directors also organize events, reach out to potential members, and communicate with current members to keep them informed and involved. Ultimately, their job is to help the organization grow and thrive by building a strong and active membership base.

A new media manager is someone who uses social media and other online platforms to help promote a company or organization. They create content like posts, videos, and graphics to share with people online. They also interact with followers, respond to comments and messages, and keep track of how well their posts are doing. Basically, they help make sure that a company gets noticed on the internet and stays connected with their audience.

A communication manager is responsible for overseeing an organization’s internal and external communication strategies. This involves creating and implementing communication plans to effectively relay information to employees, stakeholders, and the public. They work closely with various departments to ensure consistent messaging and branding across all channels, including social media, press releases, and marketing materials. Communication managers also monitor and analyze feedback to continuously improve communication efforts and maintain a positive reputation for the organization. Overall, their role is crucial in maintaining strong relationships and promoting transparency within the organization.

A union event manager is responsible for planning, organizing, and executing events for a labor union. They work closely with union leaders and members to determine event objectives, create event budgets, and coordinate all logistics such as venue selection, catering, entertainment, and promotional materials. Additionally, they oversee event staff and ensure that all activities run smoothly and efficiently. Overall, a union event manager plays a vital role in bringing union members together, fostering community spirit, and promoting the goals and values of the union.

A union organizer who does external organizing plays a very important role in helping workers come together to fight for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. They go out into the community and talk to workers at different companies, helping them understand the benefits of joining a union. By organizing workers from multiple workplaces, they can create a stronger voice that can demand changes from employers. Union organizers also help workers understand their rights and work together to make sure those rights are protected. Overall, the role of a union organizer doing external organizing is crucial in empowering workers and fighting for better conditions in the workplace.

The role of a union organizer doing internal organizing is really important because they help organize and support the workers in their own workplace. They talk to workers about their rights, help them understand the benefits of being in a union, and work together to make sure everyone is treated fairly and gets a fair wage. The union organizer also helps bring people together to stand up for their rights and make sure their voices are heard by the company. Overall, the union organizer plays a big role in making sure workers are treated well and have a say in their own workplace.
In labor relations, the primary remedies available to labor unions include collective bargaining, strikes, picketing, boycotts, filing grievances through the grievance and arbitration process, and seeking legal action through the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) to address unfair labor practices by employers, ultimately aiming to secure better working conditions and wages for their members.

Unions play a significant role in advocating for workers’ rights and ensuring fair treatment in the workplace. One important tool that unions use to address workplace grievances is the grievance process. However, the grievance process can often be a frustrating and ineffective mechanism for addressing workers’ concerns.
Firstly, the grievance process is often bogged down by bureaucratic red tape and lengthy procedures. This can make it difficult for workers to have their concerns addressed in a timely manner, resulting in prolonged disputes and unresolved issues. As a result, workers may feel discouraged and disheartened by the process, leading to a decrease in morale and productivity.
In addition, the grievance process can often favor employers over workers. Employers may have more resources and legal expertise to navigate the process, putting workers at a disadvantage. This imbalance of power can make it challenging for workers to successfully resolve their grievances and achieve a fair outcome.
Furthermore, the grievance process can be a daunting and intimidating process for workers to navigate. Workers may fear retaliation from their employers for raising grievances, causing them to remain silent about their concerns. This culture of fear can prevent workers from speaking up and seeking redress for workplace injustices.
Moreover, the grievance process can be a time-consuming and emotionally draining experience for workers. Workers may have to attend multiple meetings, gather evidence, and participate in investigations, all while trying to juggle their work responsibilities. This can take a toll on workers’ mental and emotional well-being, adding to the already stressful nature of the workplace.
Additionally, the outcomes of the grievance process can often be unsatisfactory for workers. Even if a grievance is upheld, the remedies may be minimal or insufficient to address the harm done to the worker. This can leave workers feeling like their concerns have been dismissed or ignored, diminishing their trust in the union and the grievance process.
Moreover, the lack of transparency in the grievance process can also be a source of frustration for workers. Workers may not be kept informed about the progress of their grievance or the reasons behind certain decisions. This lack of communication can erode confidence in the process and make workers feel like their voices are not being heard.
Furthermore, the grievance process can be costly for workers, both financially and emotionally. Workers may have to pay legal fees or other expenses to pursue their grievances, putting a strain on their finances. Additionally, the stress and anxiety of going through the grievance process can take a toll on workers’ mental health and well-being.
In conclusion, the grievance process can be a challenging and frustrating experience for workers, with many obstacles and barriers that can hinder their ability to seek justice and resolution. It is important for unions to work towards improving the grievance process and making it more accessible, transparent, and responsive to workers’ needs. By addressing these shortcomings, unions can better support workers and ensure that their voices are heard and their rights are protected in the workplace.

Unions play a vital role in advocating for the rights and interests of workers, but sometimes conflicts and issues arise that may lead to the filing of a grievance. However, there are several proactive steps a union can take to prevent the need for filing a grievance in the first place. One of the most important ways a union can avoid grievances is by establishing clear and effective communication channels between workers and management. By fostering an open and transparent dialogue, misunderstandings and conflicts can be addressed and resolved before they escalate into grievances.
In addition to effective communication, unions can also work towards creating a positive and cooperative relationship with management. Building mutual trust and understanding can help prevent conflicts from arising in the first place. By collaborating with management to find solutions to issues, unions can demonstrate their willingness to work towards a common goal of improving working conditions and ensuring fair treatment for all employees. This proactive approach can help prevent grievances by addressing potential problems early on and promoting a harmonious work environment.
Furthermore, unions can also invest in training and education programs for their members to ensure they are aware of their rights and responsibilities in the workplace. By providing workers with the knowledge and skills they need to effectively advocate for themselves, unions can empower their members to address issues proactively and prevent grievances from occurring. By taking a proactive stance and implementing strategies to foster communication, collaboration, and education, unions can work towards creating a positive and productive work environment where grievances are minimized.

Labor management meetings are a crucial aspect of ensuring the success and efficiency of a union. In order to get the most out of these meetings, it is important for unions to come prepared and organized. This means having a clear agenda outlining the topics to be discussed, as well as any relevant data or information that may be needed. By doing so, unions can ensure that the meeting stays focused and productive, and that all necessary information is readily available for discussion.
In addition to being prepared, it is also important for unions to foster open communication and collaboration during labor management meetings. This means providing all members with the opportunity to voice their opinions and concerns, and actively listening to all perspectives. By creating a culture of open dialogue and mutual respect, unions can work together with management to address issues and find solutions that benefit both parties. This collaborative approach not only strengthens relationships within the workplace, but also leads to more effective decision-making and problem-solving.
Finally, unions can maximize the effectiveness of labor management meetings by following up on action items and monitoring progress. After a meeting has taken place, it is crucial for unions to track the implementation of any decisions made and hold both parties accountable for following through on commitments. By regularly checking in on progress and addressing any obstacles that may arise, unions can ensure that the agreements reached during labor management meetings are upheld and that desired outcomes are achieved. Overall, by being prepared, fostering open communication, and following up on action items, unions can get the most out of labor management meetings and contribute to the overall success of their organization.

When faced with a hostile employer during labor management, it is important to approach the situation professionally and tactfully. First and foremost, it is essential to remain calm and composed, even when met with hostility. By maintaining a level head, you can better assess the situation and determine the best course of action to address the issue at hand. It is also crucial to communicate effectively with the employer, expressing your concerns and grievances in a clear and respectful manner. By articulating your points effectively, you can work towards finding a resolution that is satisfactory for both parties.
In addition to effective communication, it may be helpful to seek support from a neutral third party, such as a human resources representative or a labor union representative. These individuals can provide guidance and support in navigating the situation with a hostile employer. They can also offer advice on how to address the issue and advocate on your behalf if necessary. Seeking outside support can help ensure that your rights are protected and that the situation is handled in a fair and professional manner.
Overall, when faced with a hostile employer during labor management, it is important to approach the situation thoughtfully and strategically. By remaining calm and composed, effectively communicating your concerns, and seeking support from neutral third parties, you can work towards finding a resolution that is satisfactory for all parties involved. Remember that addressing a hostile employer can be challenging, but by taking a proactive and professional approach, you can navigate the situation with confidence and integrity.

Mediation is a process in which a neutral third party facilitates communication and negotiations between two parties in conflict in order to help them reach a mutually acceptable agreement. When it comes to labor disputes between a union and an employer, mediation can be a highly effective tool for resolving issues and improving the relationship between the two parties. The mediator helps the union and the employer clarify their respective interests, identify common ground, and explore potential solutions to the issues at hand.
During the mediation process, the mediator works with both the union and the employer to establish ground rules for the negotiation, maintain a respectful and constructive dialogue, and address any barriers to communication that may arise. The mediator helps the parties identify and prioritize their interests, explore creative solutions, and craft a mutually acceptable agreement that meets the needs of both sides. In some cases, the mediator may also facilitate separate caucuses with each party to help them consider their options, generate new ideas, and assess the potential consequences of different courses of action.
Ultimately, mediation between a union and an employer can help build trust, improve communication, and create a more positive and productive relationship between the two parties. By providing a safe and structured environment for dialogue and negotiation, mediation can help the union and the employer address their differences, find common ground, and reach agreements that benefit both sides. Through effective communication, collaboration, and problem-solving, mediation can help prevent costly and disruptive labor disputes, promote mutual understanding, and support a more harmonious and cooperative relationship between the union and the employer.

Arbitration is a method used to resolve disputes between a union and an employer outside of the traditional court system. In the context of labor relations, arbitration involves a neutral third party, known as an arbitrator, who listens to both sides of the dispute and makes a decision on how to resolve it. The arbitration process typically begins with the union and employer agreeing on a list of potential arbitrators, from which one is selected to preside over the case.
Once the arbitrator is selected, both the union and employer present their arguments and supporting evidence before the arbitrator. The arbitrator then considers the evidence presented by both sides and issues a binding decision, usually within a set timeframe. This decision is typically based on the terms of the existing collective bargaining agreement between the union and employer, as well as relevant labor laws and precedents. The decision of the arbitrator is final and legally binding, meaning that both the union and employer must abide by it.
Overall, arbitration serves as an effective tool for resolving disputes between unions and employers in a fair and impartial manner. By providing a neutral third party to evaluate the arguments and evidence of both sides, arbitration helps to ensure that disputes are resolved in a timely and efficient manner. Additionally, arbitration can help to preserve the ongoing relationship between the union and employer by providing a formal and structured process for resolving conflicts. Overall, arbitration is a vital component of the labor relations process and plays a crucial role in maintaining a harmonious and productive working environment for both unions and employers.

In the realm of labor relations, mediation serves as a crucial tool for resolving disputes between unions and management. To ensure that a union gets the most out of the mediation process, there are several key strategies that can be employed. Firstly, it is essential for the union to thoroughly prepare for the mediation session. This includes identifying the desired outcomes, gathering relevant information and evidence, and understanding the strengths and weaknesses of their position. By being well-prepared, the union can effectively articulate their interests and negotiate from a position of strength during the mediation process.
Secondly, effective communication is vital in maximizing the benefits of mediation for the union. This involves not only clearly articulating their position and interests, but also actively listening to the other party and seeking to understand their perspective. By fostering open and honest communication during mediation, the union can build trust and rapport with the other party, which can ultimately lead to more productive negotiations and a greater likelihood of reaching a mutually acceptable resolution.
Lastly, it is important for the union to approach mediation with a collaborative and problem-solving mindset. Rather than viewing it as a zero-sum game where one party wins at the expense of the other, the union should aim to find creative and mutually beneficial solutions that address the underlying issues at hand. By focusing on finding common ground and working towards a win-win outcome, the union can create a more positive and constructive mediation process that is more likely to result in a successful resolution. Ultimately, by utilizing these strategies and approaches, a union can effectively navigate the mediation process and achieve the most favorable outcomes for their members.

When a union encounters a bad faith employer during mediation, it can present significant challenges in reaching a resolution. A bad faith employer may engage in tactics such as delaying negotiations, providing misleading information, or refusing to consider the union’s proposals in good faith. Despite these obstacles, unions can still take action to address the situation and work towards a fair outcome for their members.
In cases of bad faith bargaining, unions can utilize various strategies to push back against the employer’s tactics. This may include calling attention to the employer’s actions in mediation sessions, filing unfair labor practice charges with the National Labor Relations Board, or seeking legal recourse through the courts. By advocating for their rights and holding the employer accountable for their behavior, unions can demonstrate their commitment to protecting the interests of their members and upholding the principles of collective bargaining.
Ultimately, the effectiveness of the union’s efforts in dealing with a bad faith employer in mediation will depend on a variety of factors, including the strength of the union’s bargaining position, the support of its members, and the willingness of the employer to engage in good faith negotiations. While navigating such challenges can be complex and time-consuming, unions that remain steadfast in their commitment to representing their members’ interests and holding employers accountable for their actions can ultimately achieve positive outcomes in mediation and contribute to a more equitable labor-management relationship.

Unions often find themselves at a disadvantage in arbitration due to a variety of factors. One key reason for this is the way in which arbitration is structured. Arbitration typically involves a neutral third party making decisions on labor disputes, and the arbitrator is not required to strictly adhere to the terms of the collective bargaining agreement. This can lead to outcomes that may not align with the interests of the union, as arbitrators have the flexibility to consider factors beyond the contract itself. In addition, the arbitration process can be complex and time-consuming, putting a strain on union resources and potentially leading to outcomes that favor the employer.
Furthermore, unions may struggle in arbitration due to limited bargaining power. Employers often have greater financial resources and legal expertise than unions, allowing them to present stronger arguments and evidence in arbitration proceedings. This power imbalance can make it difficult for unions to effectively advocate for their members’ interests and secure favorable outcomes in arbitration. Additionally, unions may face challenges in demonstrating the merits of their case to arbitrators, especially if they lack access to the necessary expertise or resources to effectively present their arguments.
Finally, the outcome of arbitration may also be influenced by external factors beyond the control of the union. Arbitrators may have their own biases or preconceptions that can impact their decision-making process, and employers may also exert pressure on arbitrators to rule in their favor. Additionally, the broader political and economic climate can also play a role in shaping arbitration outcomes, with arbitrators potentially being more inclined to side with employers in uncertain or unfavorable economic conditions. Overall, the combination of structural challenges, power imbalances, and external influences can make it difficult for unions to prevail in arbitration proceedings.

Union solidarity days are important initiatives that promote unity among members and showcase the strength of the union. One way to demonstrate this unity is by asking members to wear the same color on a designated day. This simple act of solidarity can create a sense of belonging and pride among members, showing that they are all united in their goals and values. By wearing the same color, members can visually display their support for each other and their common cause, sending a powerful message of solidarity to both the union and the larger community. So, next time you hear about a union solidarity day, don’t forget to wear the assigned color and show your support for your fellow union members.

On Union Solidarity Days, workers at a workplace may choose to participate in sickouts to protest unfair working conditions or to demand better wages and benefits. Sickouts are a way for employees to show solidarity and support for their fellow coworkers and to send a message to management that they are unified in their demands for change. While sickouts can be effective in drawing attention to worker grievances, they can also be risky as employees may face consequences such as disciplinary action or even termination. It is important for workers to carefully consider the potential consequences before participating in a sickout and to work together with their union to negotiate for better working conditions in a more strategic and productive manner.

Union information pickets are a way for workers to peacefully protest and raise awareness about issues like unfair wages or working conditions. To make them effective, it’s important to have clear signage and messages that highlight the specific concerns of the workers. It’s also crucial to picket in strategic locations where the picket line will be easily seen by passersby or those entering the workplace. Additionally, having a strong social media presence can help spread the message even further and garner support from the community. By organizing and executing pickets in a thoughtful and organized way, workers can increase visibility for their cause and potentially bring about positive change in their workplace.
A strike vote is a way for members of a union to show their solidarity and willingness to take action in order to achieve better working conditions or higher wages. By participating in a strike vote, union members are able to send a strong message to their employers that they are prepared to walk off the job if necessary. This can give the union more bargaining power during negotiations, as the threat of a strike can motivate employers to make concessions in order to avoid disruptions to their operations. In this way, a strike vote can help to protect workers’ rights and improve their overall job security.


The Evolution of Labor Unions: From Triumph to Compromise
In the sprawling landscape of American labor history, few narratives resonate as profoundly as the story of labor unions. From the 1930s through the 1970s, unions were at the forefront of advocating for workers’ rights, achieving significant advancements in wages, benefits, and job security for their members. However, since the 1980s, a noticeable shift has occurred. Unions began engaging in a practice often referred to as “horse trading,” where they would concede certain demands in exchange for other gains. This article explores how labor unions transitioned from a position of strength to one of compromise, and whether there is a path back to impactful negotiations for the collective bargaining table.
Historical Context: The Golden Age of Unions
The mid-20th century is often regarded as the golden age of labor unions in the United States. This era saw a robust labor movement that successfully pressed for fair wages, safe working conditions, and reasonable working hours. The passage of pivotal legislation, including the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA) in 1935, empowered unions and provided legal frameworks to protect workers’ rights to organize and bargain collectively. This conducive environment allowed labor to negotiate contracts that often favored workers significantly—pensions were secured, healthcare benefits were expanded, and living wages became a standard expectation.
The Shift: Entering the Era of Compromise
The landscape began to shift in the 1980s, as economic changes, political landscapes, and social attitudes toward labor unions evolved. Several factors contributed to this transition:
- Economic Changes: The United States experienced a paradigm shift towards globalization and a service-oriented economy. Manufacturing jobs, which were once the backbone of union membership, declined significantly. As industries moved overseas seeking lower labor costs, union strength dwindled.
- Political Climate: The rise of conservative political movements during this era led to less favorable legislation for unions. Policies promoting deregulation and reduced government intervention created a more challenging environment for collective bargaining.
- Unions’ Strategic Choices: Faced with increasing competition and pressure on employers, union leaders began adopting a more conciliatory approach. Horse trading, wherein unions would make concessions to secure some benefits, became a common tactic. While this strategy aimed to preserve jobs and benefits in a difficult landscape, it often resulted in diminished bargaining power and the erosion of previously secured gains.
Evaluating the Impact of Compromise
While the practice of horse trading has allowed some unions to secure short-term gains, it has had long-term repercussions. Many workers, particularly in lower-wage sectors, find themselves facing stagnant wages, eroded benefits, and job insecurity. Unions have become increasingly cautious, often prioritizing survival over advancing robust agendas that seek transformative change.
Moreover, the narrative around labor unions has shifted, resulting in a decline in public perception and support. As the experience of unions has become synonymous with compromise rather than victory, younger generations of workers may feel disillusioned about the role of unions in fighting for their rights.
Pathways to Recovery: Reclaiming Bargaining Power
While the challenges facing labor unions today are significant, there are pathways to regaining lost ground at the bargaining table:
- Solidarity and Unity: Renewing the emphasis on solidarity within unions is vital. By fostering stronger collaboration among union members, unions can present a united front to employers, enhancing their bargaining power.
- Grassroots Mobilization: Engaging in grassroots efforts can reignite worker enthusiasm and participation. Initiatives that localize issues, promote dialogue among members, and raise awareness about union benefits can galvanize support.
- Leveraging New Technologies: Modern technology offers unions new ways to communicate and organize. By utilizing digital platforms for mobilization, organizing campaigns, and information sharing, unions can reach wider audiences and cultivate solidarity efficiently.
- Advocacy for Policy Changes: Unions must advocate for policy changes that support labor rights, such as legislation that strengthens collective bargaining and protects workers from unfair employment practices.
- Focus on Future Generations: Involving younger workers in union activities ensures that the future of labor remains vibrant and relevant. Tailoring messaging and initiatives to address the evolving landscape of work, including gig economy challenges, can attract new members to unions.
Conclusion
Labor unions have experienced a significant transformation from their earlier days of unyielding strength to a more negotiable approach to contract bargaining. The shift towards compromise, while sometimes necessary, has diluted unions’ power and left many workers feeling vulnerable. However, by embracing strategies that promote solidarity, grassroots activism, and modernization, labor unions have the potential to reclaim their influence and once again achieve significant gains for their members. The revival of the labor movement relies not just on the negotiation table but also on the collective desire to forge a more equitable and just workplace for all workers.




Unions have long been a stalwart force in advocating for workers’ rights and protections in the labor market. However, in recent years, they have faced challenges in engaging their members and building a cohesive movement. Factors such as declining membership rates, the rise of anti-union legislation, and changing demographics in the workforce have all contributed to this struggle. Alongside these challenges, unions also face internal issues such as bureaucratic inefficiencies and lack of transparency, which can hinder their ability to effectively mobilize and unify members. In order to overcome these obstacles and revitalize the labor movement, unions must adopt more innovative and inclusive strategies to engage with their members, address their needs, and ultimately build a stronger and more unified movement for workers’ rights.

The practice of unions selling out the unborn during negotiations is a complex ethical issue that has far-reaching consequences. At its core, this practice involves unions making concessions that may benefit current members, but have negative implications for future generations of workers who are not yet part of the union. This short-term focus often ignores the long-term impact on the labor market and the broader society. As graduate students, we must critically examine the ethical implications of such actions and advocate for a more sustainable approach that considers the interests of all stakeholders, including those who are not yet born. By addressing this issue with foresight and integrity, unions can better uphold their responsibility to protect the rights and well-being of all workers, both present and future.

Unionizing low wage workers can be a strategic move to increase membership and collective bargaining power, rather than solely focusing on immediate wage gains. By organizing and mobilizing workers at the grassroots level, unions can create a strong voice and advocate for better working conditions, benefits, and job security. This can lead to improved job satisfaction and retention rates, ultimately strengthening the union’s presence and ability to negotiate for higher wages in the long run. By prioritizing the expansion of membership and solidarity among low wage workers, unions can build a sustainable platform for advocating for fair compensation and labor rights, benefiting not only current members but also future generations of workers in similar industries.

Unions have long been a stalwart force in advocating for workers’ rights and protections in the labor market. However, in recent years, they have faced challenges in engaging their members and building a cohesive movement. Factors such as declining membership rates, the rise of anti-union legislation, and changing demographics in the workforce have all contributed to this struggle. Alongside these challenges, unions also face internal issues such as bureaucratic inefficiencies and lack of transparency, which can hinder their ability to effectively mobilize and unify members. In order to overcome these obstacles and revitalize the labor movement, unions must adopt more innovative and inclusive strategies to engage with their members, address their needs, and ultimately build a stronger and more unified movement for workers’ rights.
In February 1996, Philip Morris purchased a tobacco factory on the grounds of a former extermination camp. Here, inside three of the same buildings used by the SS to torture and execute prisoners from the first transports to Auschwitz, the world’s largest tobacco company manufactured billions of cigarettes.

Coal mine owners have a long history of using violent tactics to prevent workers from unionizing. Many owners view unions as a threat to their profits and control over the mine, so they have resorted to extreme measures to discourage workers from organizing. One of the most shocking tactics that some mine owners have used is having workers killed in order to send a message to others who may be considering joining a union.
The practice of killing workers to prevent unionization is not only morally reprehensible, but it is also illegal. These actions are a blatant violation of workers’ rights and show a complete disregard for human life. Instead of addressing workers’ concerns and working towards a resolution, mine owners have chosen to resort to violence in order to maintain their power and control. This behavior is not only harmful to workers, but it also perpetuates a cycle of fear and oppression in the coal mining industry.
In order to combat this issue, it is crucial that workers stand together in solidarity and continue to push for their right to organize. By raising awareness of the injustices that workers face in the coal mining industry, we can work towards holding mine owners accountable for their actions and ensuring that workers are able to unionize without fear of retaliation. It is important for students, as future leaders and activists, to educate themselves on labor rights and advocate for fair treatment of workers in all industries. Only through collective action and perseverance can we create a more equitable and just working environment for all.

Jeff Bezos and Elon Musk are two of the wealthiest individuals in the world, known for their companies Amazon and Tesla, respectively. However, despite their massive wealth, both Bezos and Musk have been criticized for their efforts to prevent their workers from unionizing. This has earned them the label of “billionaire union busters” by many labor activists.
One of the main reasons why Bezos and Musk have been accused of being union busters is their opposition to workers forming unions in their companies. Unions are organizations that are formed by workers to collectively bargain for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. By preventing their workers from unionizing, Bezos and Musk are able to maintain more control over their employees and avoid potential increases in labor costs.
Despite facing criticism for their anti-union activities, Bezos and Musk have continued to resist efforts by their workers to form unions. This has led to protests and strikes at Amazon warehouses and Tesla factories, with workers demanding better treatment and representation. The actions of Bezos, Musk, and other billionaire union busters have raised concerns about the power and influence that these individuals have over the labor market and the need for stronger protections for workers’ rights.

In the late 1800s, Wells Fargo, a prominent banking and shipping company in the American West, took on the role of law enforcement by offering bounties for wanted outlaws. This practice of offering rewards for capturing or killing criminals was not uncommon during this time period, as there was a lack of formal law enforcement in many areas of the Wild West. Wells Fargo’s decision to put bounties on outlaws was a strategic move to protect their assets and ensure the safety of their employees and customers.
By offering bounties on outlaws, Wells Fargo was able to incentivize individuals to take on the dangerous task of apprehending or eliminating these dangerous criminals. The promise of a monetary reward provided a strong motivation for bounty hunters to track down wanted outlaws, regardless of the risks involved. In doing so, Wells Fargo was able to effectively combat crime in the often lawless frontier towns where they operated, helping to maintain order and protect the interests of the company and the communities they served.
The practice of offering bounties on outlaws by Wells Fargo was not without controversy, as it raised ethical questions about vigilante justice and the potential for abuse of power. However, in the absence of proper law enforcement infrastructure, companies like Wells Fargo had to take matters into their own hands to protect their interests and maintain the safety of their operations. While the bounty system may seem archaic by today’s standards, it was a necessary and effective tool in the fight against crime in the untamed territories of the American West.

Ray Kroc, often credited as the founder of McDonald’s, did not actually create the fast-food empire from scratch. In fact, the original McDonald’s brothers, Dick and Mac McDonald, opened the first McDonald’s restaurant in San Bernardino, California. Kroc, a businessman and franchising agent, saw the potential of their efficient system and bought the company from them in 1961. This move was controversial as many viewed it as Kroc essentially stealing the concept of McDonald’s and taking credit for its success.
Furthermore, Kroc’s stance on minimum wage and the treatment of workers has also been a point of contention. Kroc believed in keeping labor costs low in order to maximize profits, leading to his opposition to raising the minimum wage. In fact, Kroc famously fought against the introduction of a federal minimum wage increase in the late 1960s, arguing that it would hurt small businesses and slow economic growth. This viewpoint sparked criticism and protests from labor rights activists who viewed Kroc as prioritizing profits over the well-being of his employees.
In conclusion, while Ray Kroc played a significant role in transforming McDonald’s into a global powerhouse, his methods and beliefs have been met with scrutiny and criticism. From the questionable acquisition of the company to his stance on minimum wage, Kroc’s actions have stirred controversy and debate. Ultimately, Kroc’s legacy is tarnished by allegations of theft and exploitation, highlighting the complexities of business ethics and corporate responsibility in the fast-food industry.

Steve Jobs, the co-founder and former CEO of Apple Inc., is often credited with revolutionizing the tech industry with his innovative products, most notably the iPhone. However, the dark side of Apple’s success lies in the horrible conditions in which iPhones are built. Reports have emerged over the years detailing the harsh working conditions in Apple’s factories, particularly those in China, where workers are subjected to long hours, low pay, and unsafe working conditions.
Despite Apple’s claims of ensuring fair labor practices in its supply chain, the reality is that workers in iPhone factories are often exploited and mistreated. In some cases, workers have reported being forced to work overtime without compensation, being exposed to toxic substances without proper protection, and even being subjected to physical and verbal abuse by supervisors. These conditions raise serious ethical concerns about the production of iPhones and call into question the values and principles upheld by Apple as a company.
As consumers, we have a responsibility to be aware of the impact our purchasing decisions have on the lives of others. By turning a blind eye to the horrible conditions in which iPhones are built, we are essentially condoning the exploitation of workers and perpetuating a system of injustice. It is essential for companies like Apple to prioritize ethical production practices and ensure that workers are treated fairly and with dignity. As consumers, we must hold companies accountable for their actions and demand transparency and accountability in their supply chains. Only then can we truly enjoy the benefits of technological innovation without compromising the well-being of others.

Bill Ackman, J.M. Pearson, and Valent are all well-known investors who have made significant profits in the pharmaceutical industry. In recent years, there has been controversy surrounding their investments in companies that produce drugs for rare diseases, particularly those with high price tags. Critics argue that these investors are profiting off of the suffering of dying people by capitalizing on the high demand for life-saving medications.
One example of this controversy is Bill Ackman’s investment in Valeant Pharmaceuticals, a company known for acquiring smaller drug companies and drastically raising the prices of their products. Ackman’s hedge fund, Pershing Square Capital Management, profited immensely from its investment in Valeant, despite the company’s questionable business practices. Similarly, J.M. Pearson has been criticized for his investments in companies that produce medications for rare diseases, such as Turing Pharmaceuticals, which famously increased the price of a life-saving drug by over 5,000%.
While it is true that these investors have made substantial profits from their investments in pharmaceutical companies, it is important to recognize that the high prices of these drugs are often a result of the significant research and development costs required to bring them to market. However, the ethical implications of profiting off of the suffering of dying people cannot be overlooked. As graduate students, we must consider not only the financial implications of our investments, but also the ethical and moral consequences of profiting off of vulnerable populations. In the case of Bill Ackman, J.M. Pearson, and Valent, it is clear that their investments have raised important questions about the role of investors in the pharmaceutical industry and the impact of their actions on the lives of those in need.

John D. Rockefeller was a billionaire and industrialist who made his fortune in the oil industry in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was known for his ruthless business tactics and monopolistic practices that helped him become one of the wealthiest men in the world. However, Rockefeller’s success came at a cost to the workers who toiled in his factories and refineries.
Rockefeller was a notorious union buster who fought against the labor movement and crushed attempts by workers to organize and improve their working conditions. He believed that unions were a threat to his business interests and used any means necessary to suppress their efforts. Rockefeller’s anti-union stance led to numerous strikes and labor disputes that resulted in violence and suffering for the workers.
Despite his immense wealth and power, Rockefeller’s actions as a union buster ultimately hurt the workers who helped build his empire. By suppressing their right to organize and negotiate for fair wages and working conditions, he perpetuated a system of exploitation and inequality that left many workers struggling to make ends meet. While Rockefeller may have been a successful businessman, his legacy is tarnished by the harm he caused to the working class.

As a former union president, Ronald Reagan had a unique perspective on labor unions when he became the President of the United States in 1981. However, many believe that his policies and decisions during his time in office significantly hurt unions in America. One of the most notable actions taken by Reagan was his decision to fire thousands of air traffic controllers who went on strike in 1981. This move set a precedent for employers to take a tough stance against union strikes, weakening the bargaining power of unions across the country.
Additionally, Reagan’s economic policies, often referred to as “Reaganomics”, favored big business and corporations over the interests of workers and unions. His administration implemented tax cuts for the wealthy and deregulated industries, leading to a decline in wages and job security for many workers. These policies created an environment where unions struggled to protect the rights and benefits of their members, ultimately weakening their influence and power in the workforce.
Overall, Reagan’s time as President had a lasting impact on the labor movement in the United States. Many believe that his actions and policies set the stage for the decline of unions and the rise of corporate power in the country. While some may argue that Reagan’s decisions were necessary for economic growth and prosperity, it cannot be denied that his presidency had a detrimental effect on the strength and stability of labor unions in America.

During Trump’s first term, his administration took numerous actions that were not beneficial for unions, workers, and the planet. One of the most significant moves was the repeal of the Fair Pay and Safe Workplaces Executive Order, which required federal contractors to report and rectify labor violations. This allowed companies to potentially exploit workers without repercussions, leading to poorer working conditions and lower wages for many Americans. Additionally, Trump’s administration weakened labor unions by supporting right-to-work laws and appointing anti-union officials to key positions, making it harder for workers to organize and advocate for better wages and working conditions.
Furthermore, Trump’s policies on the environment were detrimental to the planet. His administration rolled back numerous environmental regulations, including the Clean Power Plan and fuel efficiency standards, which put the environment at risk and contributed to worsening climate change. By prioritizing the interests of corporations over environmental protection, Trump’s policies led to increased pollution and harm to ecosystems, further endangering the health and well-being of both current and future generations. Additionally, his decision to withdraw the United States from the Paris Agreement sent a message to the world that the country was not committed to combating climate change, further hindering global efforts to address this pressing issue.
Overall, Trump’s first term was marked by policies that prioritized the interests of corporations over the needs of workers and the planet. By dismantling labor protections and environmental regulations, his administration not only undermined the rights and well-being of workers but also contributed to the degradation of the environment. Moving forward, it is crucial for leaders to prioritize the needs of workers, support labor unions, and take meaningful action to address climate change in order to create a more equitable and sustainable future for all.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
The Cost Off Living Increase
Over The Last 30 Years


The rich can afford to be progressive,
poor people have reasin to be afraid of the future.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Westchester County, NY has seen a significant increase. This rise in expenses can be attributed to various factors such as inflation, increasing property taxes, and rising housing costs. For residents of Westchester County, this increase in the cost of living has made it harder to make ends meet and has put a strain on their financial well-being.
One major contributing factor to the increase in the cost of living in Westchester County is the rising property taxes. Property taxes in the county have been steadily increasing over the years, putting added financial pressure on homeowners. These higher property taxes have resulted in increased housing costs, which in turn have made it more difficult for residents to afford living in the area. As a result, many residents have had to make sacrifices in order to keep up with the rising costs of living in Westchester County.
In addition to property taxes, inflation has also played a role in the increasing cost of living in Westchester County. Over the past 30 years, the prices of goods and services in the county have continued to rise, making it more expensive for residents to afford basic necessities. This rise in inflation has made it increasingly challenging for residents to maintain their standard of living, leading to financial hardships for many in the area. Overall, the cost of living in Westchester County has seen a significant increase over the past 30 years, making it more difficult for residents to afford the expenses associated with living in the area.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Putnam County, NY has seen a significant increase. This means that the amount of money needed to cover basic necessities like housing, food, and transportation has gone up over time. This rise in the cost of living has put a strain on many residents, especially those who have fixed incomes or are struggling to make ends meet.
One of the main factors contributing to the increase in the cost of living in Putnam County is the rise in housing prices. As the population in the county has grown and demand for housing has increased, the prices of homes and rental properties have gone up significantly. This has made it more difficult for residents to find affordable housing, leading to an increase in homelessness and overcrowding in some areas.
In addition to housing, the cost of food and transportation has also seen an increase in Putnam County over the past 30 years. The prices of groceries and gas have gone up, making it more expensive for families to put food on the table and commute to work or school. This has put a strain on household budgets and forced many residents to make tough choices about where to allocate their limited funds. Overall, the cost of living in Putnam County has risen steadily over the past three decades, making it increasingly difficult for residents to make ends meet.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Dutchess County, NY has significantly increased. This means that the prices for basic necessities like food, housing, and transportation have gone up, making it more expensive for people to live in the area. For example, in the 1990s, the average rent for a one-bedroom apartment in Dutchess County was much lower compared to today, where rent prices have skyrocketed. This increase in cost of living has put a strain on many residents, especially those with lower incomes.
The rising cost of living in Dutchess County has also affected the affordability of owning a home in the area. Home prices have steadily increased over the years, making it harder for people to purchase a home and build equity. As a result, many residents are forced to rent apartments or houses rather than becoming homeowners. This can have long-term financial implications, as owning a home is often seen as a key factor in building wealth and financial stability.
In addition to housing costs, other expenses like healthcare and education have also seen significant increases in Dutchess County over the past few decades. Healthcare costs, in particular, have risen, putting a strain on families and individuals who need access to medical care. Similarly, the cost of education, including college tuition, has become a major financial burden for many residents. Overall, the cost of living increase in Dutchess County has had a profound impact on the daily lives and financial well-being of its residents.
The cost of living in Rockland County, NY has increased significantly over the last 30 years. This means that prices for everyday items like groceries, gas, and housing have gone up, making it more expensive for people to live in the area. One of the main reasons for this increase is the booming economy in Rockland County, which has led to higher demand for goods and services, driving up prices. Additionally, factors such as inflation and rising property values have contributed to the overall rise in the cost of living.
For residents in Rockland County, the cost of living increase over the last 30 years has had a major impact on their daily lives. Many people have had to make budget cuts and sacrifices in order to afford basic necessities. For example, some may have had to downsize to a smaller home or cut back on dining out in order to make ends meet. The rising cost of living has also made it more difficult for some individuals to save money for things like college tuition or retirement, further straining their financial situation.
Overall, the cost of living increase in Rockland County has made it more challenging for residents to maintain their standard of living. While the area offers many amenities and opportunities for its residents, the rising prices have made it harder for some people to take advantage of them. As the cost of living continues to rise, it will be important for individuals and families to carefully budget and plan in order to navigate the financial challenges of living in Rockland County.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Orange County, NY has increased significantly. This means that things like housing, transportation, food, and utilities have all become more expensive for residents in the area. For example, the average price of a home in Orange County has more than doubled since 1990, making it increasingly difficult for families to afford a place to live. In addition, the cost of groceries and gasoline has also gone up, putting a strain on people’s budgets.
One of the reasons for the increase in cost of living in Orange County over the past three decades is inflation. Inflation is the rise in prices of goods and services over time, and it can erode the purchasing power of a person’s income. As prices go up, people have to spend more money to buy the same things, leading to a higher cost of living. Additionally, the demand for housing in Orange County has increased as the population has grown, leading to higher prices for homes and rental properties.
The rising cost of living in Orange County has had a significant impact on residents, particularly those with lower incomes. Many families are struggling to make ends meet as they try to keep up with the increasing prices of basic necessities. Some people have had to make sacrifices, such as cutting back on expenses or taking on extra jobs, in order to afford their cost of living. As the cost of living continues to rise, it is important for policymakers to address this issue and work towards creating more affordable housing options and increasing wages to help residents in Orange County thrive.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in the Hudson Valley region of New York has significantly increased. This rise in living expenses has been felt by many residents in the area, leading to financial hardships for some families. One of the main factors contributing to this increase is the rising cost of housing. As demand for housing in the Hudson Valley has grown, so too have prices, making it difficult for many residents to afford a place to live.
Another major contributor to the cost of living increase in the Hudson Valley is the rising cost of goods and services. From groceries to healthcare to utilities, the prices of everyday items have steadily increased over the past three decades. This has put a strain on many residents’ budgets, forcing them to cut back on expenses or find additional sources of income to make ends meet. As a result, many families in the Hudson Valley have had to make difficult choices when it comes to their finances.
In conclusion, the cost of living in the Hudson Valley region of New York has risen significantly over the past 30 years, making it increasingly difficult for residents to afford basic necessities. As housing prices and the cost of goods and services continue to climb, many families in the area are facing financial challenges. It is important for policymakers and community leaders to address these issues and work towards solutions that can help alleviate the burden of the rising cost of living in the Hudson Valley.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in New York City has increased significantly. This means that it is more expensive to live in the city now than it was three decades ago. With prices rising for essentials like housing, groceries, and utilities, residents of NYC have had to spend more of their income on basic needs. This has made it harder for many people to make ends meet and maintain a good quality of life.
One major factor contributing to the increase in the cost of living in NYC is the rising housing prices. Rent and home prices in the city have skyrocketed over the past few decades, making it difficult for many residents to afford a place to live. This has led to an increase in homelessness and overcrowding as people struggle to find affordable housing. Additionally, the cost of groceries and other daily necessities has also gone up, further straining the budgets of NYC residents.
Overall, the cost of living increase in NYC over the last 30 years has had a significant impact on the city’s residents. Many people are finding it harder to afford basic necessities and are struggling to make ends meet. It is important for policymakers to address these issues and work towards making NYC a more affordable place to live for all its residents.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living on Long Island, New York has significantly increased. This means that it now costs more money to live on Long Island compared to three decades ago. One of the biggest factors contributing to this increase is the rising cost of housing. In the past 30 years, housing prices on Long Island have skyrocketed, making it more difficult for people to afford to buy or rent a home.
In addition to housing prices, other expenses such as food, transportation, and healthcare have also increased over the years. This means that people living on Long Island now have to spend more of their income on basic necessities compared to before. These rising costs can be challenging for individuals and families, especially those who are on fixed incomes or have lower paying jobs. It can also make it harder for younger people to save up to buy their own homes or start their own families.
Overall, the cost of living increase on Long Island over the past 30 years has had a significant impact on the community. It has made it more difficult for people to make ends meet and has forced many to make sacrifices in order to afford the basics. As prices continue to rise, it is important for individuals and families to budget carefully and find ways to save money in order to navigate the high cost of living on Long Island.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in the Capital District of New York has steadily increased. This has resulted in financial challenges for many residents in the area, as they struggle to keep up with rising prices for necessities such as housing, food, and healthcare. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the cost of living in the Capital District has increased by nearly 30% since 1990, significantly outpacing the rate of inflation.
One of the main factors driving the increase in the cost of living in the Capital District is the rising cost of housing. The demand for housing in the area has increased due to a growing population and a strong economy, which has resulted in higher prices for both rental properties and homes for sale. As a result, many residents are finding it increasingly difficult to afford housing in the Capital District, leading to a rise in homelessness and housing insecurity.
In addition to housing, the cost of food, healthcare, and transportation has also increased significantly in the Capital District over the past 30 years. This has put a strain on the budgets of many residents, particularly those with lower incomes. As a result, some residents have had to make difficult decisions about how to allocate their limited resources, such as cutting back on healthcare expenses or sacrificing other necessities in order to make ends meet. Overall, the increase in the cost of living in the Capital District has had a significant impact on the financial well-being of many residents, highlighting the need for policies to address affordability and ensure that all residents can access the basic necessities of life.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in the Mohawk Valley region of New York has steadily increased. This has had a significant impact on residents, as they have had to stretch their budgets to cover essential expenses such as housing, groceries, and transportation. This increase in living costs has made it more challenging for individuals and families in the area to make ends meet, leading to a decrease in overall financial stability.
One of the main factors contributing to the rise in the cost of living in the Mohawk Valley over the past three decades is inflation. As prices for goods and services have increased, residents have seen their purchasing power decrease, making it more expensive to maintain their standard of living. Additionally, the region has experienced changes in industries and job opportunities, which have impacted residents’ ability to earn a competitive income in line with the rising costs of living.
As a result of the cost of living increase in the Mohawk Valley, many residents have had to make sacrifices and adjustments to their lifestyles. Some have had to take on additional work or seek out higher paying jobs, while others have had to cut back on discretionary expenses in order to afford essential necessities. This has created financial stress and strain for many individuals and families in the region, highlighting the importance of addressing economic disparities and finding solutions to help alleviate the burden of rising living costs.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in the North Country region of New York has increased significantly. This rise in expenses has had a profound impact on the residents of the area, making it increasingly difficult to afford necessities such as housing, food, and healthcare. This trend has forced many individuals and families to make difficult choices and sacrifices in order to make ends meet.
One of the main factors contributing to the increase in the cost of living in the North Country is the rising cost of housing. As demand for housing continues to outpace supply, rental and housing prices have skyrocketed, making it increasingly unaffordable for many residents. Additionally, the cost of groceries and other essential items has also risen steadily over the years, putting further strain on households already struggling to make ends meet. The cost of healthcare has also increased, making it difficult for some residents to access the medical care they need.
Overall, the increase in the cost of living in the North Country over the past 30 years has had a significant impact on the residents of the region. Many individuals and families are finding it increasingly difficult to afford basic necessities, leading to financial strain and stress. As the cost of living continues to rise, it is crucial for policymakers and community leaders to address these challenges and work towards creating a more affordable and sustainable future for all residents of the North Country.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Central New York has steadily increased, making it more expensive for residents to meet their basic needs. This increase in the cost of living has affected many aspects of daily life, including housing, groceries, and healthcare. For example, the average rent for an apartment in Central New York has more than doubled in the past three decades, making it difficult for many individuals and families to afford a decent place to live.
In addition to the rising cost of housing, the price of groceries and other everyday essentials has also gone up significantly over the years. This means that residents of Central New York have to spend a larger portion of their income on food and other basic necessities, leaving less money for other expenses such as transportation or entertainment. Furthermore, the cost of healthcare in the region has also increased, making it harder for individuals to afford necessary medical treatments and services.
Overall, the cost of living increase in Central New York over the past 30 years has had a significant impact on the financial well-being of its residents. As prices continue to rise, many people are finding it increasingly difficult to make ends meet and maintain a decent standard of living. It is important for policymakers and community leaders to address these issues and work towards creating more affordable living options for the residents of Central New York.

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in the Southern Tier of New York has significantly increased. This has impacted many residents in the region, making it more challenging to afford basic necessities such as housing, food, and transportation. Factors contributing to the rising cost of living include inflation, housing market trends, and changes in economic conditions.
One of the main reasons for the cost of living increase in the Southern Tier can be attributed to inflation. Inflation refers to the general increase in prices of goods and services over time. As the cost of living rises, the purchasing power of individuals decreases, making it harder to make ends meet. Additionally, the housing market in the region has also experienced substantial growth, leading to higher rents and property prices. This has put a strain on individuals and families, especially those with lower incomes.
Furthermore, changes in economic conditions, such as job availability and wages, have also impacted the cost of living in the Southern Tier. While the region has seen some economic growth in recent years, many residents still struggle to find well-paying jobs. This disparity between job opportunities and living expenses has made it difficult for individuals to keep up with the rising cost of living. Overall, the cost of living increase in the Southern Tier of New York has presented challenges for many residents, highlighting the need for policies and initiatives to address these issues and support those in the region.

The cost of living in the Finger Lakes region of New York has increased significantly over the past 30 years. This has been observed in various aspects of life, such as housing, groceries, utilities, and transportation. For example, the median home price in the Finger Lakes has more than doubled from $80,000 in 1990 to over $200,000 in 2020. This has made it increasingly difficult for families and individuals to afford to purchase a home in the area.
Additionally, the cost of groceries and utilities has also seen a significant increase. A gallon of milk, for example, has gone from $2.50 in 1990 to over $4.00 in 2020. Similarly, the average monthly utility bill has risen from $100 in 1990 to over $200 in 2020. These rising costs have put a strain on many residents in the Finger Lakes region, especially those on fixed incomes or lower-wage jobs.
The increase in the cost of living has also impacted transportation expenses. Gas prices have more than doubled in the past 30 years, going from $1.20 per gallon in 1990 to over $3.00 per gallon in 2020. This has made it more expensive for individuals to commute to work or travel around the region. Overall, the rising cost of living in the Finger Lakes over the past 30 years has made it increasingly challenging for residents to make ends meet and maintain a decent quality of life

Over the past 30 years, the cost of living in Western New York has significantly increased. This means that it now costs more money for basic necessities such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare. Many families in the region are feeling the burden of these rising costs as their salaries have not kept up with inflation, making it harder to make ends meet.
One of the major factors contributing to the increase in cost of living in Western New York is the rising cost of housing. Real estate prices have surged over the past few decades, making it more difficult for individuals and families to afford homes. Rent prices have also increased, putting a strain on those who cannot afford to buy a house. This has led to a higher percentage of income being spent on housing, leaving less money for other expenses.
In addition to housing, the cost of healthcare and education have also risen significantly in Western New York over the past 30 years. Medical expenses have skyrocketed, making it difficult for individuals without adequate insurance to afford necessary treatments. Similarly, the cost of higher education has increased, leading to more student loan debt for young adults. These rising costs have put a strain on many families in the region and have led to increased financial stress for many residents.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

When considering the cost of living in New York State, it’s essential to evaluate the financial requirements for various household types, including a single person, a family of three, and a family of four. For a single individual, the average monthly expenses can range from approximately $3,000 to $4,000, primarily driven by housing costs, which account for around 30% of total expenses. In contrast, a family of three may incur monthly costs between $6,000 and $8,000, factoring in additional expenses such as childcare and healthcare. For families of four, this figure can escalate to approximately $8,000 to $10,000 per month due to increased food and educational needs. It is important to note that these estimates can vary significantly based on specific location within the state, lifestyle choices, and housing arrangements. Understanding these financial dynamics is crucial for effective budgeting and planning for those considering relocation or evaluating their current living situation in New York State. For more detailed insights into managing living costs effectively, consider exploring local resources and financial planning services.

When evaluating the cost of living in Western New York, it is essential to consider the financial implications for different household types, including a single person, a family of three, and a family of four. For a single individual, monthly expenses typically range from $2,500 to $3,000, encompassing housing, utilities, groceries, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may expect to incur costs around $4,500 to $5,500 per month due to increased needs for space, food, and childcare. Meanwhile, a family of four can anticipate monthly expenses between $5,500 and $7,000, influenced by factors such as educational expenses and healthcare needs. These estimates reflect the diverse economic landscape of Western New York, where housing costs can vary significantly depending on the specific location within the region. Understanding these financial requirements is crucial for individuals and families considering relocation or budgeting in this area. For more detailed insights into specific neighborhoods and their associated costs, further research is recommended.

When assessing the cost of living in the northern region of New York, it’s crucial to consider various factors that impact financial requirements for different household sizes. For a single person, monthly expenses typically range from $2,500 to $3,500, encompassing rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may require approximately $4,500 to $6,000 per month, while a family of four generally faces costs between $5,500 and $7,500. These estimates reflect the varying expenses associated with housing markets in cities such as Plattsburgh and Watertown, where rental prices and local amenities can significantly influence overall affordability. Additionally, factors such as childcare, healthcare, and education play a pivotal role in determining the total financial commitment for families. Understanding these dynamics is essential for potential residents or families considering relocation to this region. To better navigate these financial considerations, it is advisable to conduct thorough research or consult local resources for more tailored budgeting advice.

The cost of living in the Mid-Hudson region of New York varies significantly depending on household composition. For a single person, the average monthly expenses, including rent, utilities, and groceries, can range from $2,500 to $3,000. In contrast, a family of three typically incurs higher costs, approximately $4,500 to $5,500 per month, as they require larger living spaces and more resources. Meanwhile, a family of four may see their monthly expenses rise to between $5,500 and $7,000, driven by increased demands for housing, healthcare, and educational expenses. These figures highlight the financial considerations necessary for residents in this region to maintain a comfortable lifestyle. Understanding these costs is crucial for prospective movers or current residents looking to budget effectively. Therefore, for anyone contemplating a move to the Mid-Hudson area or assessing their financial situation, it is essential to conduct thorough research and consider all variables involved in these living expenses.

When evaluating the cost of living in the New York City region, it is essential to consider different household configurations. For a single person, monthly expenses typically range from $3,000 to $4,500, accounting for rent, utilities, transportation, and groceries. A family of three can expect to spend approximately $6,500 to $9,000 monthly, while a family of four’s expenses generally fall between $7,500 and $12,000. These estimates highlight the substantial financial commitment required to reside in this metropolitan area, where housing costs often dominate the budget. Additionally, factors such as lifestyle choices and location within the city can significantly influence these figures. Individuals and families contemplating a move to New York City should meticulously analyze their financial situation and explore various neighborhoods to optimize their living expenses effectively. For a comprehensive understanding of potential costs tailored to specific circumstances, further research and budgeting are advisable.

Living in the Long Island region of New York presents varying costs depending on the household size, specifically for a single person, a family of three, or a family of four. For a single individual, the estimated monthly expenses typically range between $3,000 to $4,000, which encompasses rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may incur costs approximately between $7,000 and $9,000 monthly due to increased housing needs and child-related expenses. For families of four, the financial demands increase further, averaging around $9,000 to $12,000 per month. These estimates reflect essential living expenses; however, factors such as lifestyle choices, housing location within Long Island, and schooling options can significantly influence overall costs. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for anyone considering relocation to this region. For more detailed insights tailored to your specific situation, we encourage you to explore comprehensive cost-of-living resources.

The cost of living in New Jersey varies significantly based on family size and lifestyle choices, making it essential to analyze the financial requirements for different household compositions. For a single person, the average monthly expenses can range from $3,000 to $4,000, depending on factors such as housing, transportation, and personal expenditures. A family of three typically incurs higher costs, averaging between $6,000 and $8,000 per month, which includes expenses for childcare and education alongside standard living costs. In contrast, a family of four may face a budget of approximately $8,000 to $10,000 monthly, factoring in additional needs like groceries, healthcare, and recreational activities. Understanding these financial dynamics is crucial for prospective residents and can aid in effective budgeting strategies. To ensure comprehensive financial planning, individuals and families should consider consulting local resources or financial advisors that specialize in New Jersey’s economic landscape.
When considering the cost of living in Connecticut, it is essential to analyze the financial requirements for different household structures, specifically a single person, a family of three, and a family of four. For a single individual, average monthly expenses can range from approximately $3,000 to $4,000, accounting for housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and healthcare. In contrast, a family of three may expect to spend between $7,000 and $9,000 monthly due to increased costs associated with childcare and educational expenses. For a family of four, the financial burden escalates further, with estimates suggesting monthly living costs could reach upwards of $10,000. These figures highlight the significant financial commitment required to reside in Connecticut. Therefore, individuals and families should meticulously budget and plan their finances to ensure sustainable living in this state. For more detailed insights into budgeting for life in Connecticut, consider consulting local financial resources or experts.

When evaluating the cost of living in Pennsylvania, it is essential to consider the financial requirements for different household sizes. For a single person, monthly expenses typically range from $2,500 to $3,000, accounting for housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and health care. In contrast, a family of three generally faces a higher cost of living, with estimates averaging between $4,500 and $5,500 per month. This increase primarily reflects additional expenditures on food, childcare, and educational resources. For families of four, the monthly budget can escalate to approximately $5,500 to $6,500, factoring in similar costs as those for a family of three but with further allowances for larger housing needs and increased consumption. These estimates can vary significantly based on specific locations within Pennsylvania, lifestyle choices, and personal financial management strategies. Understanding these costs is crucial for individuals and families planning to relocate or budget effectively in Pennsylvania; thus, prospective residents are encouraged to conduct thorough research tailored to their unique circumstances.

The cost of living in Massachusetts can vary significantly depending on the household size and location within the state. For a single person, monthly expenses typically range from $3,000 to $4,000, accounting for rent, utilities, food, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may require approximately $7,000 to $9,000 per month to maintain a similar standard of living, factoring in additional costs such as childcare and education. Meanwhile, a family of four can expect to budget around $8,500 to $11,000 monthly, reflecting the increased financial demands associated with housing, healthcare, and daily necessities. These estimates underscore the importance of thorough financial planning when considering relocation to or residing in Massachusetts. For individuals or families contemplating their options in this region, it is advisable to conduct further research into specific towns and cities to obtain a more tailored understanding of living costs.

The cost of living in the New York City metro area varies significantly based on household composition, specifically for a single person, a family of three, and a family of four. For a single individual, monthly expenses typically range from $3,000 to $4,000, factoring in rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may require between $6,000 and $8,000 per month to maintain a comparable standard of living, as additional costs such as childcare and education come into play. For families of four, these monthly expenses can escalate further to approximately $8,000 to $10,000 due to the need for larger housing accommodations and increased food and healthcare costs. Understanding these financial implications is crucial for potential residents or those considering relocation within the metropolitan area. To navigate the complexities of budgeting in New York City effectively, prospective movers should conduct thorough research and possibly consult with local experts to ensure informed decision-making regarding their housing and lifestyle choices.

When considering the cost of living in New York’s Capital Region, it is essential to analyze the financial requirements for different household types, specifically a single person, a family of three, and a family of four. For a single individual, monthly expenses typically range from $2,500 to $3,000, accounting for rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. In contrast, a family of three may require approximately $5,000 to $6,000 per month to maintain a comfortable lifestyle, factoring in additional costs such as childcare and healthcare. Meanwhile, a family of four generally faces expenses that can reach upwards of $7,000 to $8,500 monthly, influenced by increased housing costs and educational needs. These figures demonstrate the significant financial commitment necessary for varying household sizes within the Capital Region. For those contemplating relocation or budgeting strategies in this area, understanding these costs is crucial for effective financial planning and ensuring a sustainable living environment.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

When considering the cost of living in the Hudson Valley region of New York compared to New York City, there are several key factors to take into account. The Hudson Valley, located just north of the bustling metropolis of New York City, offers a more suburban and rural lifestyle with lower costs of living in many aspects. From housing prices to everyday expenses, comparing the two areas can give a clearer picture of where one may be able to stretch their dollar further.
One of the most significant differences between the cost of living in the Hudson Valley and New York City is the housing market. In New York City, the average rent for a one-bedroom apartment can easily exceed $3,000 per month, while in the Hudson Valley, the same size apartment may only cost around $1,500 – $2,000 per month. This stark contrast in housing prices can make a significant impact on one’s budget and overall quality of life.
In addition to housing prices, everyday expenses also vary between the two regions. In New York City, the cost of groceries, dining out, and transportation expenses can be higher than in the Hudson Valley. With a more suburban lifestyle in the Hudson Valley, residents may have access to more affordable grocery options and dining establishments, which can help offset some of the higher housing costs in the area.
Furthermore, healthcare costs can also differ between the Hudson Valley and New York City. While both regions offer top-tier medical facilities and services, the overall cost of healthcare in New York City may be higher due to the demand and competition for services. In the Hudson Valley, residents may find more affordable healthcare options with lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Overall, when comparing the cost of living in the Hudson Valley to New York City, it is clear that there are notable differences in housing prices, everyday expenses, and healthcare costs. While New York City may offer a more vibrant and fast-paced urban lifestyle, the Hudson Valley provides a more affordable suburban and rural alternative for those looking to save money and live a more relaxed lifestyle. Understanding these differences can help individuals make informed decisions about where to live based on their financial situation and personal preferences.

The cost of living is a crucial factor to consider when choosing a place to reside. In this essay, I will compare the cost of living in the Hudson Valley, NY to Long Island. The Hudson Valley is a region located in New York State, known for its picturesque landscapes and historic attractions, while Long Island is an island in the state of New York, just east of Manhattan. Both areas offer unique opportunities and amenities, but there are differences in the cost of living that individuals should be aware of when deciding where to live.
One of the major factors that contribute to the cost of living in the Hudson Valley is housing expenses. In recent years, the housing market in the Hudson Valley has seen a significant increase in prices due to high demand and limited inventory. According to recent data, the average cost of a home in the Hudson Valley is around $400,000. On the other hand, Long Island has a higher average home price of around $500,000. This means that individuals looking to purchase a home in the Hudson Valley may find more affordable options compared to Long Island.
In addition to housing expenses, the cost of groceries and other goods and services also play a role in the overall cost of living. In the Hudson Valley, the cost of groceries is relatively lower compared to Long Island. The cost of a gallon of milk, a loaf of bread, and a dozen eggs are all cheaper in the Hudson Valley compared to Long Island. Additionally, the cost of dining out and entertainment options may be more affordable in the Hudson Valley compared to Long Island, where prices can be higher due to the proximity to New York City.
Another important factor to consider when comparing the cost of living in the Hudson Valley to Long Island is transportation costs. In the Hudson Valley, the cost of owning a car and gas expenses may be higher compared to Long Island, where public transportation options are more readily available. However, the overall cost of commuting may be lower in the Hudson Valley, as the average commute time is shorter compared to Long Island. Individuals should take into consideration their transportation needs when comparing the cost of living in both areas.
Overall, the cost of living in the Hudson Valley and Long Island can vary depending on individual preferences and needs. While the Hudson Valley may offer more affordable housing options and lower grocery prices, Long Island may provide better public transportation options and access to a wider variety of amenities. It is essential for individuals to carefully consider their budget and lifestyle needs when deciding where to live. Both the Hudson Valley and Long Island offer unique opportunities and experiences, and individuals should weigh the pros and cons of each area before making a decision on where to reside.
When comparing the cost of living between Dutchess County and Westchester County in New York, there are several key factors to consider. One of the first things to take into account is housing costs. In Westchester County, the average home price is significantly higher than in Dutchess County, making it more expensive to purchase or rent a property in this area. Additionally, the cost of utilities and groceries tends to be higher in Westchester County, leading to an overall higher cost of living in this region.
Another important aspect to consider when comparing the cost of living in Dutchess and Westchester County is transportation costs. Westchester County has a more developed public transportation system, including trains and buses, which can be a more affordable option for residents. In contrast, Dutchess County has limited public transportation options, leading to higher costs for owning and maintaining a personal vehicle. Additionally, the cost of fuel and tolls may be higher in Westchester County due to its proximity to New York City.
Overall, while both Dutchess and Westchester County offer desirable living experiences in New York, the cost of living tends to be higher in Westchester County due to higher housing prices, transportation costs, and overall expenses. Individuals looking to reside in Westchester County should be prepared for a larger financial commitment compared to those living in Dutchess County. It is important for individuals to carefully consider their budget and financial priorities when deciding where to live in these two counties in New York.

When comparing the cost of living between Dutchess and Putnam County in New York, several factors must be considered. One major factor is the cost of housing. In Dutchess County, the median home value is around $300,000, whereas in Putnam County, the median home value is closer to $350,000. This difference in housing costs can have a significant impact on overall cost of living, as housing is often one of the biggest expenses for individuals and families.
Another important factor to consider when comparing the cost of living between Dutchess and Putnam County is the cost of groceries and other daily necessities. In general, Putnam County tends to have slightly higher prices for groceries and other essential items compared to Dutchess County. This can add up over time and contribute to a higher cost of living in Putnam County.
Additionally, transportation costs can also vary between the two counties. Dutchess County has a more developed public transportation system, which can help residents save money on gas and car maintenance expenses. Putnam County, on the other hand, may require residents to rely more heavily on their own vehicles, leading to higher transportation costs overall. In conclusion, while both Dutchess and Putnam County have relatively high costs of living compared to other areas in New York, Dutchess County may offer slightly lower costs in terms of housing, groceries, and transportation.

Cost of living can vary greatly depending on the location, and when comparing Putnam County to Westchester County in New York, significant differences can be seen. Putnam County generally has a lower cost of living compared to Westchester County. This is mainly due to the fact that housing prices are typically cheaper in Putnam County than in Westchester County. Other factors that contribute to the lower cost of living in Putnam County include lower property taxes, lower utility costs, and lower overall expenses for groceries and other basic necessities.
On the other hand, Westchester County is known for having a higher cost of living compared to Putnam County. This is partly due to Westchester County’s proximity to New York City, which is a major financial and cultural hub. The strong job market in Westchester County also contributes to the higher cost of living, as residents are willing to pay more for the convenience of living closer to their workplace. Additionally, the larger population and higher demand for housing in Westchester County drive up property prices and overall expenses for residents.
Overall, when comparing the cost of living between Putnam County and Westchester County, it is clear that Westchester County is the more expensive option. While both counties offer beautiful landscapes and a high quality of life, those looking for a more affordable living situation may find Putnam County to be a more suitable choice. However, for those who prioritize convenience and are willing to pay a premium for it, Westchester County may be the better option despite the higher cost of living. Ultimately, the decision on where to live should be based on personal preferences and financial circumstances.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
The Rising Cost of Living: A 30-Year Perspective on New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and the United States
The cost of living is a crucial factor affecting the quality of life for residents across the United States. Over the last three decades, New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and the broader U.S. have all experienced significant increases in living expenses. This article examines how these regions have fared over the past 30 years, focusing on notable trends, contributing factors, and the implications for residents.
A Historical Overview
In the early 1990s, the economic landscape of the United States was markedly different. The country was emerging from a recession, with inflation rates relatively stable, and the housing market was more accessible than today. However, starting in the late 1990s and into the early 2000s, the tech boom fueled economic growth, and with it, property values and living costs soared, particularly in metropolitan areas.
Regional Breakdown
New York
New York City, known for its high cost of living, saw housing prices skyrocket over the past three decades. The median home price in the city skyrocketed from approximately $150,000 in the 1990s to nearly $700,000 today. Rents have also surged, with many neighborhoods witnessing increases of over 100%. Factors contributing to this rise include demand from both domestic and international buyers, economic opportunities, and gentrification.
New Jersey
New Jersey has experienced similar trends, with property taxes among the highest in the nation. Over the last 30 years, the median home price has nearly tripled, driven by its proximity to New York City and Philadelphia. While some areas have seen significant urban renewal, towns with good school systems and transportation links have become particularly desirable, pushing costs further upward.
Connecticut
Connecticut’s cost of living reflects a mix of high-income households and challenges in affordability. Although often seen as a haven for affluent residents, the state has faced economic headwinds leading to stagnant wages for many, even as housing prices remained high. Connecticut’s median home price rose from around $165,000 in the 1990s to roughly $350,000 today, exacerbating the affordability crisis.
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania presents a somewhat different picture. While areas like Philadelphia have seen rising costs, particularly in desirable neighborhoods, other parts of the state have lagged behind. On average, the state has maintained a lower cost of living compared to its northeastern neighbors, although trends indicate that urban areas are experiencing similar inflation in housing.
Massachusetts
Massachusetts, particularly Greater Boston, has seen some of the most significant increases in the cost of living, driven by a booming tech industry and prestigious educational institutions. The median home price has surged from around $175,000 in the 1990s to over $600,000 today, creating a challenging environment for new homebuyers and renters alike.
National Trends
Across the United States, the cost of living has generally risen due to factors such as inflation, rising housing costs, healthcare expenses, and educational costs. According to data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) has increased by approximately 110% since 1990, a significant rise that underscores the challenges faced by American consumers.
Contributing Factors
- Supply and Demand: In many urban areas, the demand for housing has outstripped supply, leading to bidding wars and inflated prices.
- Economic Growth: Regions that have experienced job growth, especially in high-paying sectors like technology and finance, have seen living costs rise in tandem with income growth.
- Inflation and Interest Rates: Over the last 30 years, inflation and fluctuating interest rates have affected the cost of goods and services, making budgeting more challenging.
- Policy Decisions: Local and state policies, including zoning laws and tax regulations, have impacted housing availability and affordability, contributing to exaggerated increases in living costs.
- Demographic Shifts: Migration patterns, with individuals moving from less expensive areas to urban centers, have compounded demand in already competitive markets.
Implications for Residents
The steep increase in living costs presents numerous challenges for residents in these regions. Many families find it increasingly difficult to afford housing, leading to a rise in the number of households spending more than 30% of their income on rent – a commonly accepted measure of housing affordability.
In addition, as wages have not kept pace with inflation, workers are feeling the pinch. The middle class, in particular, is at risk of being squeezed out of many desirable neighborhoods. Furthermore, young professionals and families are increasingly reconsidering their options, with some opting to relocate to more affordable areas, which could impact local economies and community structures.
Conclusion
The rising cost of living in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and across the United States reflects broader economic shifts, challenges in housing availability, and demographic changes over the last 30 years. As these trends continue, it is crucial for policymakers, communities, and individuals to address the implications of rising costs and work toward solutions that promote affordability and quality of life for all residents. Understanding this complex landscape is essential as we navigate the reality of living in an increasingly expensive environment.

Title: A 30-Year Projection: The Cost of Living Increase in the Northeastern United States
Introduction
The cost of living is a critical factor impacting individuals and families in their daily lives, influencing everything from housing and food to healthcare and transportation. As we look ahead to the next 30 years, projections indicate that the cost of living will rise significantly across the United States, with particularly pronounced increases expected in New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, and Massachusetts. Understanding these projections can help residents and policymakers prepare for the economic realities that lie ahead.
National Trends in Cost of Living
The overall cost of living in the United States is projected to increase by approximately 2.5% annually over the next three decades, resulting in a cumulative increase of around 100% by 2053. Several factors contribute to this trend, including inflation, rising wages, an aging population, and evolving consumer preferences. Economic models suggest that certain sectors, such as healthcare and housing, will see the most substantial increases.
Cost of Living Projections in the Northeast
While the national average provides a contextual background, the Northeastern states mentioned here may face even steeper cost increases.
- New York: New York City, as one of the most expensive cities in the world, is expected to see a cost of living increase of around 3% annually. This could mean that by 2053, residents may experience a near doubling of living expenses, particularly due to skyrocketing housing prices, high taxes, and increasing demand for services.
- New Jersey: Known for its high property taxes and competitive housing market, New Jersey could see a similar increase to New York, at approximately 2.8% per year. Many towns are already experiencing affordability crises, and this trend may accelerate as more people will continue to migrate to suburban areas for affordable housing.
- Connecticut: Connecticut has been grappling with economic challenges, including outmigration and stagnating wages. Projections suggest that the cost of living may rise by about 2.5% per year, impacted heavily by high property taxes and essential services.
- Pennsylvania: In Pennsylvania, particularly in urban centers like Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, the cost of living is predicted to increase by around 2.4% annually. Factors including an aging infrastructure and fluctuating education costs will contribute to these increases.
- Massachusetts: Home to prestigious universities and a bustling tech hub, Massachusetts is expected to see a cost of living increase around 2.6% each year. Housing demand driven by innovation and a talented workforce will continue to place upward pressure on living costs.
The Implications of Rising Costs
The anticipated increases in the cost of living are likely to have far-reaching implications, especially for low- and middle-income families. Key considerations include:
- Housing Affordability: As home prices climb, affordability will become a critical issue, particularly for first-time homebuyers and renters. In dense urban areas, gentrification may further marginalize vulnerable populations.
- Economic Disparities: As living expenses outpace wage growth, wealth inequality may become exacerbated. Regions may see more significant economic divides, with affluent areas thriving while others struggle to keep up.
- Migration Patterns: Prolonged increases in the cost of living may lead to shifts in population as residents seek more affordable markets. This “reverse migration” could benefit rural and suburban areas while straining urban economies.
- Mental Health and Well-being: Financial stress from rising costs can affect mental health and overall well-being, leading to increased burdens on healthcare systems and social services.
Conclusion
As we project into the future, residents of New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts, and the broader United States must prepare for an inevitable rise in the cost of living. Planning for these changes—through informed policy measures, community engagement, and financial literacy—will be crucial to ensuring that future generations can thrive amidst evolving economic landscapes. Addressing affordability issues and fostering equitable growth will require collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities to navigate the challenges ahead effectively.

Reversing the Trend: The Legacy of Labor Unions and the Challenges of Today’s Global Economy
The Rise of American Labor Unions
In the mid-20th century, the labor movement in the United States was a potent force, fundamentally reshaping the landscape of the American workplace. The 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s were marked by significant achievements for labor unions, which successfully advocated for higher wages, improved working conditions, and better benefits for workers across various industries. Unions not only elevated the standards of their members but also set benchmarks that benefited non-unionized workers through what is often referred to as the “spillover effect.” This period saw the establishment of a powerful middle class, largely attributed to a strong labor movement that secured the rights and protections workers desperately needed.
The Global Economy’s Impact on Wages
Fast forward to the present day, and many of the gains made by organized labor are increasingly under threat. The forces of globalization, characterized by the ease of trade and the movement of labor across borders, have shifted the balance of power in favor of employers. The availability of cheap labor in developing countries has exerted downward pressure on wages in the United States, as companies seek to cut costs by outsourcing jobs or hiring contingent workers who lack the representation of unions.
Moreover, the weakening of environmental laws has exacerbated this situation, allowing multinational corporations to operate with fewer restrictions and lower operational costs in countries with fewer protections for workers and the environment. This not only undermines workers’ rights domestically but also encourages a “race to the bottom,” where labor standards are compromised in pursuit of cheaper production methods.
The Challenges within the Developed World
While the plight of workers in developing countries is crucial, the situation for many American workers today is also dire. The erosion of labor unions—the very entities that fought for wage increases and better working conditions—has left many workers vulnerable. Union membership has been declining over the decades, currently hovering around 10% of the workforce. This decline has stymied collective bargaining power, leaving many workers without a seat at the negotiating table.
Low-wage jobs, precarious employment, and the gig economy have become the norms for many workers, particularly in sectors that once offered stable employment with benefits. The stagnation of wages, even as productivity has increased, raises significant concerns about the livelihoods of American workers in contrast to the values upheld by their unionized forebears.
Can We Reverse the Trend?
The question remains: can we reverse these trends that threaten the very fabric of labor rights and conditions secured over decades? While this is a complex challenge, several pathways exist to revitalize the labor movement and improve working conditions across various sectors.
- Strengthening Labor Laws: Advocating for stronger labor protections at both state and federal levels can help secure the rights of workers. Reviving and expanding measures such as the Employee Free Choice Act would facilitate union formation and protect workers from intimidation during organizing efforts.
- Promoting Fair Trade Practices: Supporting fair trade initiatives can help ensure that workers in developing countries are compensated fairly, thereby stabilizing global supply chains. This could reduce wage competition imposed by outsourcing and create a more leveled playing field for domestic workers.
- Encouraging Worker Cooperatives: Fostering the growth of worker-owned cooperatives can empower employees, offering them greater control over their workplaces and preserving more significant shares of profits within the community.
- Investment in Skills Development: Providing vocational training and education can equip American workers to compete effectively, particularly as industries evolve with technology. This can mitigate the impact of cheaper labor globally while raising the quality of jobs available domestically.
- Rallying Community Support: Building coalitions among labor unions, community groups, and consumers can intensify the movement for better working conditions. Grassroots campaigns can pressure corporations to adopt ethical labor standards and hold them accountable.
Conclusion
Reclaiming the labor gains achieved in the mid-20th century is an intricate task, especially given the multifaceted challenges posed by the global economy and systemic corporate practices. However, the spirit of collective action that defined the labor movement is still alive and can be harnessed to confront today’s issues. By advocating for fair labor practices, bolstering union protections, and promoting sustainable economic models, it is possible to reverse the trend and create a labor landscape that honors the rights of all workers—both domestic and global. The road may be long, but history proves that with unity and determination, significant change is achievable.
The American Economic Landscape: Paycheck to Paycheck, Poverty, and the Working Poor
In contemporary America, economic anxiety is prevalent, with millions of individuals and families navigating the harsh realities of financial insecurity. The terms “living paycheck to paycheck,” “below the poverty line,” and “working poor” often describe overlapping yet distinct groups within the broader socioeconomic fabric. Understanding the current statistics, historical context, and future projections related to these categories can offer vital insights into the challenges faced by Americans today.

Current State of Financial Insecurity
As of 2023, studies suggest that approximately 64% of Americans are living paycheck to paycheck, which means they rely on each paycheck to cover their immediate expenses without room for savings or emergencies. This statistic underscores a significant challenge for a majority of the population, where even a minor financial setback can lead to dire consequences.
Additionally, about 11.6% of Americans are living below the official poverty line, which is defined by the U.S. Census Bureau as an annual income of $13,590 for an individual and $27,750 for a family of four (as of 2022). This figure highlights the struggles of millions who cannot meet even the most basic needs for themselves and their loved ones.
The phenomenon of the “working poor,” those who are employed yet still struggle to attain a basic standard of living, affects around 27 million Americans. This demographic often works full-time but earns low wages without benefits like health insurance or retirement plans, exacerbating their financial challenges.
A Historical Perspective: 30 Years Ago
To understand the severity of current economic strains, it is essential to compare recent data with historical trends. In 1993, approximately 41% of Americans reported living paycheck to paycheck. The percentage of the population below the poverty line was around 14.5%, showing a slight increase compared to today’s figures. The term “working poor” was also relatively common, but comprehensive data is more sparse; estimates from that period suggested nearly 20% of full-time workers fell into this category, indicating that the issue of low wages was already a significant concern.
The economic landscape of the early ’90s was shaped by recession, high unemployment, and slow wage growth. However, shifts in both policy and economic conditions over the following decades brought about improvements in some areas while new challenges surfaced.
A Glimpse into the Future: Projections 30 Years Ahead
While it is always challenging to predict the future accurately, various economic analyses and trends allow for educated projections about the state of financial security in America by 2053. Some analysts suggest that, without substantial systemic changes, the percentage of Americans living paycheck to paycheck could rise to 75%. Factors contributing to this alarming projection include the rising cost of living, stagnating wages, and increasing economic disparities
The poverty rate, although it may fluctuate with economic conditions, could hover around 10-12% if current trends persist, particularly in the context of economic inequality and the ability of individuals to access quality education and job opportunities.
The number of working poor may also rise significantly, possibly affecting 30 million Americans or more, particularly if minimum wage laws do not adjust in accordance with inflation and the soaring cost of living. Without interventions like enhanced labor rights, living wage initiatives, and accessible education and training programs, the vision of a secure economic future remains uncertain.
Conclusion
The current statistics regarding Americans living paycheck to paycheck, below the poverty line, and as part of the working poor reveal an ongoing crisis of economic security. Historical comparisons show a troubling trend of stagnation, and projections highlight the potential exacerbation of these issues in the coming decades. Addressing these challenges requires comprehensive policy reforms, emphasizing livable wages, affordable housing, accessible healthcare, and robust education systems. Only through concerted efforts can the cycle of financial insecurity be broken and the American Dream revitalized for future generations.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

# Comparing the Cost of Living and Quality of Life: Blue States vs. Red States
In recent years, the debate surrounding the cost of living and quality of life in the United States has become increasingly pronounced, especially when contrasting blue states like New York, California, and Illinois with red states such as Florida, Texas, and Alabama. This analysis aims to delve into these differences, examining how political affiliation influences economic conditions and lifestyle options. By breaking down key factors such as housing, healthcare, education, and overall quality of life metrics, we can gain a clearer understanding of how these regions compare.
## Understanding Cost of Living
The cost of living is a crucial determinant for many individuals and families when deciding where to settle. It encompasses various expenses, including housing costs, transportation, groceries, healthcare, and taxes. Generally speaking, blue states tend to have higher living costs due to elevated housing prices and taxes.
### Housing Costs
In blue states like California and New York City, real estate prices are notoriously high. For instance, the median home price in San Francisco exceeds $1 million, whereas New York City’s average rent for a one-bedroom apartment can approach $3,000 per month. In contrast, red states such as Texas and Florida offer more affordable housing options. In cities like Austin or Orlando, you can find decent homes for significantly less—often under $400,000.
### Taxes
Taxation is another important factor that contributes to the overall cost of living. Blue states typically impose higher income taxes and sales taxes to fund public services. For example, California has a progressive income tax rate that can reach over 13%, while New York also has high state income taxes. Conversely, red states often feature no state income tax at all—like Florida—and lower overall tax burdens which can be appealing for residents looking to maximize their disposable income.
## Quality of Life Factors
While cost is an essential consideration, quality of life is equally significant. This includes access to healthcare services, education quality, job opportunities, safety levels in communities, recreational activities available to residents, and environmental factors.
### Healthcare Access
Blue states generally have more robust healthcare systems due to higher funding levels from state budgets. For instance, California’s Medi-Cal program provides health coverage to millions of low-income residents. However, this comes with its own challenges; long wait times for services are common in densely populated areas. On the other hand, while red states may have fewer resources allocated towards public health initiatives—Alabama ranks low on national health metrics—they often experience shorter wait times for medical care due to less demand.
### Education Quality
Education systems vary widely between blue and red states. Blue states like Illinois pride themselves on having some of the nation’s top-ranked public universities and K-12 systems in urban areas; however, funding disparities often exist in rural districts. Red states such as Texas also have strong educational institutions but face criticism regarding funding equity and educational outcomes across different demographic groups.
### Job Opportunities
Economic opportunity is another critical aspect influencing quality of life. Blue states tend to offer diverse job markets with high-paying positions in technology and finance concentrated in urban centers like New York City or Silicon Valley in California. Meanwhile, red states are experiencing rapid growth in sectors such as energy (Texas) and tourism (Florida), attracting new businesses that create jobs but may not always offer salaries comparable to those found in blue-state metropolitan areas.
## Conclusion: Weighing Choices
Ultimately, whether one chooses a blue state or a red state will depend on personal priorities regarding cost versus quality of life aspects. Those seeking vibrant cultural scenes and comprehensive public services might lean towards blue states despite their higher costs; conversely, individuals prioritizing affordability may find red states more attractive.
As we continue to navigate through shifting economic landscapes influenced by political affiliations across the country, it’s essential for potential movers to conduct thorough research tailored to their unique needs.
**Call to Action:** Are you considering relocating but unsure where? Take some time to evaluate your priorities—be it affordable housing or access to quality healthcare—and explore which state aligns best with your lifestyle aspirations! Share your thoughts below or reach out with any questions about specific regions!
# Comparing the Cost of Car Manufacturing in Michigan to Missouri: Wages, Benefits, and Working Conditions
The automotive industry is a cornerstone of the U.S. economy, particularly in states like Michigan and Missouri. With a rich history rooted in car manufacturing, these two states present compelling case studies when it comes to understanding the financial dynamics of the industry. This blog post delves into the cost of car manufacturing in Michigan compared to Missouri, highlighting key differences in wages, benefits, and working conditions for employees.
## The Landscape of Car Manufacturing
Michigan has long been recognized as the heart of the American automotive industry. Home to major players such as Ford, General Motors, and Stellantis, it boasts a highly developed infrastructure for car manufacturing. In contrast, Missouri has emerged as an attractive alternative for automakers looking to expand their operations. With lower operating costs and a growing workforce, Missouri’s auto sector is increasingly gaining traction.
### Cost Considerations
When examining the cost of car manufacturing between these two states, several factors come into play: labor costs, facility expenses, supply chain logistics, and regulatory environments.
-
**Labor Costs**: Labor costs are one of the most significant factors affecting manufacturing expenses. In Michigan, where unions have historically played a strong role in negotiating wages for workers in the automotive sector, average hourly wages tend to be higher than those in Missouri. As of 2023, skilled production workers in Michigan can earn upwards of $30 per hour with generous overtime provisions. In contrast, similar roles in Missouri average around $25 per hour.
-
**Benefits**: In addition to wages, benefits packages significantly impact overall compensation. Michigan manufacturers often provide comprehensive health insurance plans, retirement contributions, and other benefits due to union agreements. Conversely, while some manufacturers in Missouri offer competitive benefits packages as well, they may not be as extensive or standardized across the board.
-
**Facility Expenses**: The cost of establishing and maintaining manufacturing facilities also varies by state. Michigan’s established infrastructure can mean higher property values and utility costs but offers proximity to a dense network of suppliers and skilled laborers. Meanwhile, Missouri’s lower real estate prices may result in lower initial capital expenditures for new plants or expansions.
### Working Conditions
Working conditions are another critical aspect that differentiates these two states within the automotive sector.
-
**Union Influence**: Unions play a pivotal role in shaping working conditions within Michigan’s automotive plants. Collective bargaining agreements help ensure safe working environments and fair treatment for employees. While Missouri does have unions present within its automotive workforce, there is generally less influence compared to Michigan.
-
**Safety Standards**: Safety regulations are strictly enforced across both states; however, the level of compliance can vary depending on union presence and corporate policies. Companies operating in unionized environments often face more rigorous scrutiny regarding workplace safety protocols.
-
**Job Security**: Employees in Michigan may experience greater job security due to established contracts that protect against layoffs during economic downturns or plant closures—an assurance that may not be as prevalent in Missouri’s less unionized environment.
## Conclusion
In summary, while both Michigan and Missouri offer unique advantages within the car manufacturing landscape, they differ significantly concerning costs associated with labor and employee benefits as well as working conditions facilitated by union presence. For manufacturers considering their operational strategies or locations for expansion or relocation, these factors warrant careful consideration.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve—especially with advancements such as electric vehicles—the dynamics between states like Michigan and Missouri will undoubtedly shift further. Understanding these nuances will help stakeholders make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
### Call to Action
Are you involved in the automotive industry or considering entering this dynamic market? Share your thoughts on how regional differences affect manufacturing decisions! Engage with us by leaving comments below or following our blog for more insights on trends impacting the automotive sector across the United States.
# Comparing the Cost of Car Manufacturing in the United States to Mexico: Wages, Benefits, and Working Conditions
The global automotive industry has long been a barometer for economic conditions, labor practices, and international trade relations. In recent years, there has been increasing interest in comparing car manufacturing costs between the United States and Mexico. This comparison not only touches upon financial aspects but also delves into the wages, benefits, and working conditions for employees in both countries. Understanding these differences is critical for stakeholders in the automotive sector, policymakers, and consumers alike.
## The Cost of Car Manufacturing: A Financial Overview
When it comes to car manufacturing costs, several factors come into play, including raw materials, labor expenses, overheads, and logistics. Historically, manufacturers have shifted production to countries with lower operational costs. Mexico has emerged as a significant player in this regard due to its competitive labor market and favorable trade agreements like the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA).
In Mexico, labor costs are significantly lower than in the United States. According to recent estimates, hourly wages for assembly line workers in Mexico can range from $3 to $5 per hour compared to $25 to $30 per hour for similar positions in the U.S. This wage disparity allows manufacturers operating in Mexico to reduce their overall production costs substantially. Additionally, Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. market aids in minimizing shipping expenses and reducing lead times.
## Wages: A Closer Look
Wages are one of the most notable differences between car manufacturing operations in the U.S. and Mexico. In addition to base pay disparities, benefits associated with these wages vary dramatically as well. American workers often receive comprehensive health insurance packages, retirement plans, and paid leave that can add considerable value to their compensation packages.
Conversely, while Mexican workers may receive some benefits such as health insurance and annual bonuses (known as aguinaldo), these are generally less comprehensive than their American counterparts. Furthermore, many Mexican employees face job insecurity due to temporary contracts or lack of union representation. This precarious employment situation can lead to higher turnover rates and less experienced workforces on assembly lines.
## Working Conditions: A Comparative Analysis
Working conditions also differ significantly between the two countries. In the U.S., stringent labor laws enforce safety regulations, reasonable working hours, and employee rights protections that are designed to create a safe work environment. American automotive plants are typically equipped with advanced safety technologies and regularly undergo inspections to ensure compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards.
In contrast, while many Mexican factories adhere to basic safety guidelines mandated by law, reports suggest that enforcement can be lax. Workers may face longer hours without proper breaks or safety measures in place. Moreover, there have been accounts of inadequate ventilation and exposure to hazardous materials that raise concerns about worker health over time.
## Conclusion: The Broader Implications
The comparison of car manufacturing costs between the U.S. and Mexico encapsulates more than just economics; it brings into focus issues surrounding labor rights and ethical manufacturing practices. While lower costs in Mexico may benefit manufacturers financially, they raise important questions about worker welfare and corporate responsibility.
As consumers become increasingly aware of these disparities, there is a growing expectation for companies to prioritize ethical production practices alongside profitability. The automotive industry must navigate this complex landscape carefully—balancing cost efficiency with a commitment to fair wages and safe working conditions for all employees.
If you found this analysis insightful or wish to learn more about how global manufacturing trends affect local economies and workforce dynamics, we encourage you to explore further resources or engage in discussions on this vital topic!

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in Japan is influenced by a variety of factors, including wages and benefits to employees, taxes and government regulations, as well as the overall cost of production materials and technology. While specific numbers can change with time, I will provide a general analysis based on established data and economic principles.
- **Wages and Benefits**: Japan is known for its high labor costs, particularly due to the strong social welfare system and the tradition of lifetime employment. The average wage in Japan’s manufacturing sector is significantly higher than in many other countries. For instance, as of 2020, the average monthly wage for manufacturing employees was approximately 300,000 JPY (about $2,700 USD). Additionally, Japanese companies often provide generous benefits, such as health insurance, pensions, and bonuses, which can increase the total labor cost.
- **Taxes and Government Regulations**: Japan has a corporate tax rate of approximately 30%, which is on the higher side compared to some other major economies. Moreover, there are various other taxes and levies, including consumption tax (which applies to the sale of vehicles), environmental taxes (due to Japan’s strict emissions standards), and labor-related taxes. The country also has stringent regulations regarding safety, emissions, and quality that can add to the cost of production.
- **Cost of Production Materials**: Japan has limited natural resources and relies heavily on imports for raw materials like steel, aluminum, and oil. The fluctuation in the exchange rate of the Japanese Yen against the currencies of these exporting countries can affect the cost of materials. However, Japan is known for its efficient supply chains and strong domestic supplier networks, which can mitigate some of these costs.
- **Technological Investment**: Japanese automakers are at the forefront of technological innovation in the industry, investing heavily in areas such as electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and artificial intelligence. While these investments can be costly in the short term, they contribute to long-term competitiveness by enhancing product quality and efficiency.
Regarding Japan’s competitiveness in the global auto industry:
– **Quality and Reliability**: Japan is renowned for its high-quality automobiles. Companies like Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Mazda have built reputations for reliability and innovation, which allows them to command premium prices in the global market.
– **Efficiency and Lean Manufacturing**: The Japanese automobile industry is a pioneer of lean manufacturing practices, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory management and the Toyota Production System. These methods reduce waste and improve efficiency, contributing to competitiveness.
– **Home Market**: Japan’s large domestic market provides a strong base for these companies to build and refine their products before exporting them.
– **Technological Advancements**: Japan’s commitment to technological innovation helps its automakers maintain a competitive edge, particularly in the development of hybrid and electric vehicles.
– **Brand Recognition**: Japanese automobile brands are recognized worldwide for their quality and design, which supports their market presence and sales.
– **Economies of Scale**: Due to their large production volumes, Japanese manufacturers can achieve economies of scale, which can reduce costs per unit.
Despite the high labor costs and taxes, Japan remains competitive due to its focus on innovation, quality, and efficient manufacturing processes. However, Japan does face challenges such as a shrinking domestic market due to demographic changes and increasing competition from lower-cost producers in Asia and Europe. Additionally, trade agreements and tariffs can impact the export market.
To analyze the cost structure scientifically, one could use the concept of comparative advantage, which suggests that Japan will remain competitive in the global auto industry as long as its productivity and technology offset the higher labor costs. Moreover, the cost-plus pricing model is often employed in manufacturing, where the total cost of production (including wages, materials, taxes, and a markup for profit) is calculated and then compared with market prices to set a competitive selling price.
In conclusion, Japan’s automobile manufacturing costs are higher than some other countries due to labor costs and government regulations, but its competitiveness in the global market is sustained by its commitment to quality, technological innovation, and efficient production systems.

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in China includes various factors such as labor wages and benefits, materials, taxes, government regulations, and other operational expenses. To analyze these costs with academic rigor, we can consider several aspects:
- **Labor Costs**: China has been known for its relatively low labor costs compared to developed countries, which has been a significant factor in attracting automobile manufacturers. However, wages have been increasing in recent years due to a growing economy, urbanization, and government policies aimed at improving living standards. According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China, the average hourly wage for employees in the manufacturing sector was CNY 31.3 in 2020, which is approximately USD 4.70. Although these wages are lower than in Western nations, they are significantly higher than in some other emerging markets. Additionally, labor costs include benefits such as social security, housing funds, and other mandatory contributions, which can increase the total labor cost.
- **Material Costs**: The cost of materials for automobile production, such as steel, aluminum, rubber, and electronic components, can be influenced by global commodity prices and the domestic market in China. China has developed a substantial domestic supply chain for these materials, which can provide cost advantages due to proximity and potentially lower transportation costs. However, the quality and reliability of these materials can vary, which may affect the overall cost and competitiveness of the vehicles produced.
- **Taxes and Government Regulations**: Automobile manufacturers in China are subject to various taxes, including value-added tax (VAT), corporate income tax, and customs duties on imported parts and components. The VAT rate is generally around 16%, with some reduced rates for certain goods. The corporate income tax is set at 25%, but there are often incentives for foreign companies, particularly in certain regions or for specific industries. Moreover, China has implemented policies to encourage the production of electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids, offering tax exemptions and subsidies for these types of vehicles. This can affect the cost structure for companies focusing on these markets.
- **Other Government Regulations**: China has regulations concerning environmental standards, safety, and technology, which can influence manufacturing costs. For instance, the Chinese government has set targets for the production and sales of new energy vehicles (NEVs), which may require additional investments in research and development (R&D) and compliance costs for manufacturers. Additionally, the country has a complex system of local government incentives and regulations that can vary across provinces, affecting the overall cost of manufacturing.
- **Economies of Scale**: China has the advantage of economies of scale due to its large domestic market and extensive manufacturing capabilities. This can lead to lower per-unit costs for automakers.
- **Infrastructure**: China has invested heavily in its infrastructure, which can reduce transportation and logistics costs.
- **Exchange Rates**: Fluctuations in the exchange rate between the Chinese yuan (CNY) and other currencies, such as the US dollar, can impact the cost of exports and imports, affecting the global competitiveness of Chinese-produced vehicles.
**Competitiveness in the Global Auto Industry**:
China has become a dominant player in the global automobile industry due to several factors:
– **Cost Competitiveness**: Despite rising wages, China’s overall cost structure remains competitive due to its vast labor pool and established supply chains.
– **Government Support**: The Chinese government provides significant support to the auto industry through policies and investments in infrastructure, which can help drive down costs and encourage innovation.
– **Large Domestic Market**: China is the largest automobile market in the world, offering significant sales opportunities for domestic and foreign manufacturers.
– **Rapid Technological Advancement**: China is investing heavily in R&D, particularly in the EV sector, and is quickly closing the technology gap with established global leaders.
– **Localization**: Many international automakers have set up joint ventures with Chinese companies to access the market and reduce costs.
However, China also faces challenges such as:
– **Rising Wages**: As China’s economy matures, wages are increasing, which could erode some of its cost advantages.

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in India is influenced by various factors, including labor costs, raw materials, government regulations, and taxes. To analyze this, we can break it down into several key components:
- **Labor Costs**: India has a relatively low-cost labor force compared to many developed countries. According to the International Labor Organization, the average wage in India’s automobile manufacturing industry is significantly lower than in countries like the United States, Germany, and Japan. However, labor costs in the auto industry are rising due to increased demand for skilled labor and the implementation of higher minimum wage laws. Additionally, benefits such as healthcare, retirement, and other social security contributions add to the overall labor cost.
- **Raw Materials and Components**: The cost of steel, aluminum, plastics, and other materials necessary for car production can be affected by global commodity prices and domestic availability. India has been working on developing its local supply chain to reduce dependency on imports, which can fluctuate in price. The Make in India initiative has encouraged the growth of ancillary industries, potentially reducing the cost of components.
- **Taxes and Government Regulations**: India has a complex tax structure with various taxes levied on the production and sale of automobiles, including Goods and Services Tax (GST), customs duties, and state-level taxes. Moreover, there are regulations such as Bharat New Vehicle Safety Assessment Program (BNVSAP) and Bharat Stage (BS) emission standards that require additional investments for compliance. The GST rates for automobiles range from 18% to 28%, with additional cess based on the type of vehicle.
- **Infrastructure and Logistics**: Although India is improving its infrastructure, the cost of logistics and transportation can be relatively high due to poor road conditions, traffic congestion, and inadequate ports and rail systems. This affects the overall cost of production and distribution.
- **Economy of Scale**: As the fourth-largest car market in the world, India has the potential for economies of scale that can lower the cost of production. However, the market is highly competitive, and achieving the optimal scale can be challenging due to the presence of many small and medium-sized enterprises.
Regarding competitiveness in the global auto industry:
India has become a competitive player in the global automobile market for several reasons:
– **Cost Advantage**: As mentioned earlier, lower labor costs and a growing local supply chain provide a cost advantage to Indian automakers.
– **Skilled Workforce**: India has a large, educated, and relatively inexpensive workforce that can be trained in various aspects of automobile manufacturing, including engineering, design, and assembly.
– **Market Growth**: The growing domestic demand for vehicles, particularly in the small car and two-wheeler segments, has encouraged international companies to establish manufacturing plants in India.
– **Government Incentives**: Policies such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for the automobile and auto components industry aim to boost the production of vehicles and enhance exports.
– **Localization**: Indian automakers are increasingly localizing their production to reduce reliance on imports, which can lead to cost savings and competitive pricing in the export market.
However, there are challenges that India faces in terms of competitiveness:
– **Infrastructure**: While improvements are being made, the country’s infrastructure still lags behind that of leading auto-producing nations, affecting the cost and efficiency of manufacturing and logistics.
– **Regulations**: Complex and sometimes unpredictable regulatory environments can increase the cost of doing business and deter investment.
– **Technology**: Keeping up with technological advancements, especially in the realms of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving, requires significant investment that some Indian companies may struggle to meet.
– **Brand Perception**: Indian automobile brands may face challenges in the global market due to perceptions of lower quality compared to established international brands.
To maintain and enhance its competitiveness, India needs to focus on innovation, infrastructure development, skill enhancement, and creating a conducive business environment that encourages investment in research and development.

To provide a comprehensive analysis of the cost of manufacturing automobiles in South Korea, including wages and benefits, taxes, and government regulations, as well as an assessment of the country’s competitiveness in the global auto industry, we would need to consider various factors and sources. However, I can offer an overview based on the available data and research.
- Wages and Benefits:
South Korea is known for its skilled and educated workforce, which contributes to its competitiveness in the automobile industry. The average wage for automobile manufacturing employees in South Korea is generally higher than in many other countries but lower than in some developed nations such as Japan and the United States. However, the cost of benefits and social welfare can also be substantial. The country has a strong labor movement, and automakers are required to provide their employees with a comprehensive package that includes healthcare, pensions, and other social benefits. The total labor cost can be affected by factors such as union negotiations, the overall economy, and government policies.
- Taxes and Government Regulations:
The South Korean government provides various tax incentives and subsidies to support the automobile industry, particularly in the areas of research and development (R&D) and environmental initiatives. For instance, there are tax credits for companies that invest in eco-friendly vehicle production. However, like any other country, there are standard corporate taxes, value-added taxes (VAT), and other levies that automakers must pay. The tax rate is subject to change with government policy, but as of my knowledge cutoff in 2021, the corporate tax rate in South Korea is around 22%. Additionally, there are regulations concerning labor laws, environmental standards, and safety that can influence production costs.
- Competitiveness in the Global Auto Industry:
South Korea is one of the leading automobile producing countries globally. It is home to companies such as Hyundai Motor Group and Kia Motors, which are among the top 10 automakers in the world. The country’s competitiveness in the auto industry can be attributed to several factors:
– Economies of Scale: South Korean automakers have large production capacities that allow them to achieve cost advantages through economies of scale.
– Technology and Innovation: South Korea has a strong focus on technology and innovation, which enables its companies to produce high-quality vehicles that are competitive in global markets.
– Investment in R&D: The South Korean government actively supports R&D in the automobile sector, leading to advances in areas such as electric vehicles and autonomous driving.
– Strong Domestic Market: South Korea has a large domestic market for automobiles, which helps in achieving economies of scale and fosters innovation.
– Trade Agreements: The country has established numerous free trade agreements (FTAs) that reduce tariffs and other trade barriers, making its exports more competitive.
– Government Support: The government provides various forms of support to the automobile industry, including investment in infrastructure and favorable policies for export-oriented businesses.
However, South Korea faces challenges such as high labor costs and increasing competition from emerging markets like China and India, as well as established players in Europe and the United States. Additionally, the global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and stricter emissions regulations may require significant investments that could affect the overall cost structure of South Korean automakers.
To provide more precise and up-to-date figures on wages, taxes, and other costs, as well as a detailed comparison with other countries, one would need to conduct a thorough analysis using the latest data from industry reports, government statistics, and academic research. It’s also important to note that costs can vary significantly among different automakers and vehicle models due to differences in technology, production processes, and market strategies.

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in Germany is influenced by several factors, including wages and benefits to employees, taxes, government regulations, and the overall cost of production. To provide an in-depth analysis, let’s break down each of these components:
- **Wages and Benefits:** Germany is known for having a highly skilled workforce and a strong social welfare system, which translates into relatively high wages and substantial benefits for employees. According to the German Federal Statistical Office, the average hourly wage in the automotive industry in Germany was €42.20 in 2020. Additionally, employees typically receive a range of benefits such as health insurance, pension contributions, vacation time, and other social security payments. These benefits can add approximately 25-30% to the direct wage costs.
- **Taxes and Other Government Regulations:** The corporate tax rate in Germany is approximately 30%, which includes both federal and local taxes. However, the effective tax rate can be lower due to various deductions and tax credits. Additionally, there are other taxes such as the value-added tax (VAT) and trade taxes that auto manufacturers must account for. The German government also imposes regulations on the automobile industry concerning environmental standards, safety, and labor laws, which can add to the cost of production.
- **Production Costs:** The cost of manufacturing an automobile includes the price of raw materials, energy, logistics, and other operational expenses. As of 2020, the average cost to produce a car in Germany was estimated to be around €25,000-$35,000, depending on the model and brand. This cost includes the production of parts, assembly, research and development (R&D), and administrative expenses.
- **Competitiveness in the Global Auto Industry:**
Germany is one of the most competitive countries in the global auto industry for several reasons:
- **Innovation and Technology:** The country is a leader in automotive engineering and is home to several luxury car brands like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Porsche, and Volkswagen. The German automotive industry is known for its innovation, particularly in the areas of efficiency, quality, and advanced technology such as electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving.
- **Education and Skilled Workforce:** The German education system emphasizes vocational training, which results in a highly skilled workforce capable of producing high-quality vehicles. This human capital is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
- **Infrastructure:** Germany’s well-developed infrastructure allows for efficient supply chains and logistics, which can reduce costs and lead times.
- **Government Support:** The government provides incentives for the development of new technologies, particularly in the areas of electric vehicles and alternative fuels. This support can help offset some of the higher costs associated with manufacturing in Germany.
- **Brand Reputation:** German automakers benefit from a strong brand reputation for reliability, engineering prowess, and luxury, which allows them to charge premium prices for their products.
Despite the high wages and stringent regulations, Germany remains competitive due to its focus on innovation, productivity, and high-quality manufacturing. The country’s automakers have managed to maintain a significant market share by catering to the luxury and high-performance segments, where they can justify the higher costs of production. However, they also face increasing competition from countries with lower labor costs and governments offering substantial incentives for investment, such as China, South Korea, and some Eastern European nations. Moreover, the industry is under pressure to meet stricter emissions standards and adapt to the shift towards electric and autonomous vehicles, which require significant investments in new technologies.
To maintain competitiveness, German automakers are focusing on automation and digitalization to enhance productivity and reduce costs. They are also investing heavily in R&D to stay ahead in the race for innovation, particularly in the fields of electrification, connectivity, and autonomous driving. The German government’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and fostering an environment conducive to the development of electric vehicles will continue to play a crucial role in the industry’s future.

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in Thailand involves various factors, including wages and benefits for employees, materials, operational costs, and governmental taxes and regulations. To provide a comprehensive analysis, we will examine each of these components and then assess Thailand’s competitiveness in the global auto industry.
- Wages and Benefits:
In Thailand, the average wage in the automotive industry is relatively low compared to developed countries. However, it is essential to consider the cost of living and purchasing power parity (PPP) when making such comparisons. As of 2020, the average wage for a worker in the automotive sector was approximately THB 15,000-20,000 (about USD 450-600) per month. Benefits may include healthcare, social security, and bonuses, which can increase the total labor cost per employee. Despite the relatively low wages, Thailand’s labor productivity has been increasing, making it an attractive location for automakers seeking cost-effective manufacturing.
- Taxes and Government Regulations:
The Thai government has implemented several incentives to attract foreign investment in the automobile sector. For instance, the Board of Investment (BOI) offers tax holidays and reduced corporate income tax rates for companies that invest in specific industries, including automotive. The exact tax rates depend on the type of investment and the period. Additionally, the government has regulations in place to support the domestic automotive industry, such as the Excise Department’s eighth-tier excise tax structure that favors the production and sale of eco-friendly vehicles. The country also participates in various free trade agreements, such as the ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA), which reduce tariffs on parts and vehicles imported from other ASEAN countries, lowering production costs for automakers.
- Operational Costs:
Operational costs include factors such as land, utilities, logistics, and supply chain management. Thailand’s strategic location in Southeast Asia provides it with a robust infrastructure, including ports and roadways that facilitate the movement of goods. The country is also rich in natural resources like rubber, which is used in car parts, and has a developed automotive parts supplier base. The cost of land and utilities can vary depending on the region, with urban areas like Bangkok being more expensive than rural areas. Additionally, the Thai government often provides subsidies and investment incentives for companies that build factories in specific industrial estates.
- Competitiveness in the Global Auto Industry:
Thailand has become one of the most significant automobile manufacturing hubs in Southeast Asia, often referred to as the “Detroit of the East.” It is the largest producer of vehicles in the region and the world’s 13th largest car manufacturer. The country’s competitiveness can be attributed to several factors:
– Low labor costs and a skilled workforce: Thailand’s labor costs are lower than in countries like Japan, South Korea, and China, making it an attractive alternative for car manufacturers. Moreover, the government has invested in workforce education and training programs to enhance the skill set of the local labor pool.
– Favorable government policies: The Thai government’s policies, including tax incentives and tariff reductions, have created a conducive environment for automakers to set up production facilities.
– Strong supply chain and logistics: Thailand has a well-established supply chain for automotive parts and components, with many international suppliers present in the country.
– Proximity to growing markets: Thailand’s proximity to other ASEAN countries and the broader Asia-Pacific region allows it to serve as a production base for automakers targeting these growing markets.
– Trade agreements: The country’s participation in free trade agreements such as AFTA and the Thailand-Japan Free Trade Agreement (TJFTA) has facilitated the export of vehicles and parts to other countries with reduced tariffs.
However, challenges remain, such as increasing competition from neighboring countries like Vietnam and Indonesia, which are also developing their automotive industries, and the need for further innovation and technology adoption to maintain competitiveness in the face of global industry trends like electric vehicles (EVs) and automation.
To summarize, the cost of manufacturing automobiles in Thailand is relatively lower due to lower wages and a supportive government policy environment. The cost of wages and benefits for employees, while lower than in many developed countries, is balanced by a growing skilled workforce. Taxes and other government regulations are structured to support the industry’s growth. Thailand’s competitiveness in the global auto industry is strong due to its strategic location, cost advantages, and developed supply chain, though it faces challenges from regional competition and the need to adapt to technological changes.

The cost of manufacturing automobiles in Brazil is influenced by a variety of factors, including wages and benefits to employees, taxes, government regulations, and the overall economic landscape of the country. To provide an academically rigorous and comprehensive analysis, we would need to consider each of these elements in detail. However, I can offer a general overview based on available data and economic principles.
- Wages and Benefits to Employees:
In Brazil, the automotive industry is known for having relatively high labor costs compared to some other countries. The minimum wage is set by the government and is adjusted annually for inflation. As of 2020, the minimum wage in Brazil was approximately BRL 1,045 (Brazilian Real) per month, which is equivalent to about USD 200. However, workers in the automotive sector typically earn more than the minimum wage due to their higher skill levels and unionization rates. Additionally, Brazilian labor laws mandate generous benefits such as a 13th-month salary (a bonus equal to one month’s pay), vacation pay, and health and pension contributions from employers. These benefits can significantly increase the total labor cost.
- Taxes and Other Government Regulations:
Brazil has a complex tax system with various federal, state, and local taxes that automobile manufacturers must pay. The main taxes include the Industrial Product Tax (IPI), Value Added Tax (ICMS), and Corporate Income Tax (IRPJ). Additionally, there are taxes on imported parts and components, which can further increase the cost of production. The government also implements policies to encourage the use of locally sourced materials through incentive programs like the Inovar Auto and the Program of Development, Industry and Foreign Trade (PDE). These programs can affect the cost structure of automobile production in Brazil.
- Competitiveness in the Global Auto Industry:
Brazil is one of the largest automobile markets and producers in the world, with significant manufacturing presence from global automakers such as General Motors, Volkswagen, Ford, and Fiat Chrysler Automobiles. The country’s competitiveness in the global auto industry can be assessed through several lenses:
– Market Size: Brazil’s large domestic market has historically made it an attractive location for vehicle production, though recent economic challenges have affected demand.
– Cost of Production: High labor costs and taxes can make production less competitive compared to countries with lower labor costs and more favorable tax environments, such as Mexico or some countries in Eastern Europe and Asia.
– Infrastructure: Brazil’s extensive road network is a plus, but issues with logistics and port efficiency can add to production costs.
– Local Supply Chain: The country has developed a substantial local supply chain for automotive parts and components, which can reduce the reliance on imports and lower costs for manufacturers.
– Exchange Rate: The value of the Brazilian Real against major currencies can impact the cost of exports and imports, affecting competitiveness. A weaker Real can make Brazilian exports more attractive, while a stronger Real can increase the cost of imported components.
– Economic Conditions: The overall economic stability and inflation rates in Brazil can affect the cost of production and consumer purchasing power.
To provide a specific cost analysis, one would need to consider the detailed production costs for different models, including raw material prices, logistics, energy costs, and the impact of trade agreements and tariffs on export prices. Moreover, the competitiveness of the Brazilian automotive industry also depends on factors such as technological advancement, innovation, and the ability of firms to adapt to global market trends.
In conclusion, while Brazil has certain advantages in the global auto industry, such as a large domestic market and a developed supply chain, the high cost of labor and taxes, along with economic volatility, pose challenges to its competitiveness. A detailed cost analysis would require examining the specific conditions of each manufacturer and the models they produce, taking into account the entire value chain of automobile production.